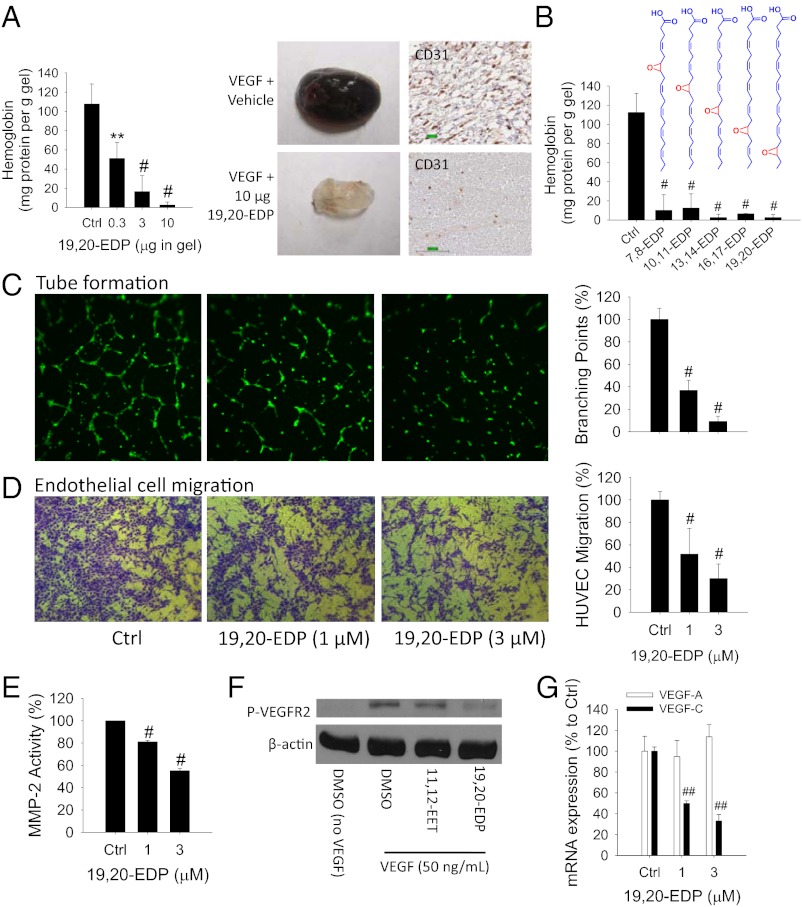
Fig. 1.
EDPs inhibit angiogenesis. (A) The 19,20-EDP inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis in a Matrigel plug assay in C57BL/6 mice in a dose-dependent manner (n = 4–6 mice per group). Dose of VEGF is 100 ng per gel. (Left) Quantification of angiogenesis using hemoglobin assay. (Right) Image of representative gels and immunohistochemistry for CD31. (B) All EDP regioisomers inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis in mice (n = 6–10 mice per group). Dose of EDP regioisomer was 10 µg per gel. (C) The 19,20-EDP inhibited endothelial tube formation after 6-h treatment in HUVECs. (Left) Calcein AM-stained HUVEC microscopy. (Right) Quantification of tube formation. (D) The 19,20-EDP inhibited VEGF-induced cell migration of HUVECs on extracellular matrix protein fibronectin after 18-h treatment in HUVECs. (Left) Crystal violet-stained HUVEC microscopy. (Right) Quantification of migrated cells. (E) The 19,20-EDP inhibited MMP activity after 4-h treatment in HUVECs. (F) At a dose of 1 µM, 19,20-EDP not 14,15-EET, inhibited VEGF-induced VEGFR2 phosphorylation after 10-min treatment in HUVECs. (G) The 19,20-EDP inhibited VEGF-C mRNA expression after 6-h treatment in HUVECs. Results are presented as means ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; #P < 0.001; ##P < 0.00001.