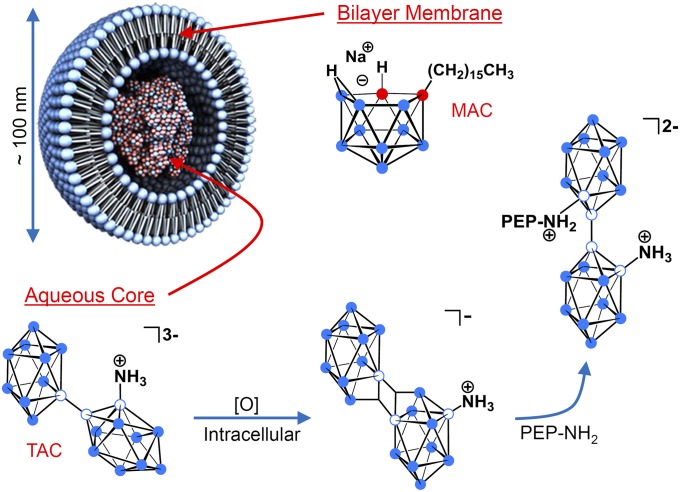
Fig. 1.
Liposomal formulation in which the lecithin/cholesterol bilayer membrane incorporates the lipophilic boron agent MAC, acting as a complement to the hydrophilic polyhedral borane TAC, which is encapsulated in the aqueous core (filled blue circle = boron-hydrogen; empty blue circle = boron; and filled red circle = carbon). Upon release from liposomes and exposure to an oxidant, [O], in the tumor cell interior, TAC undergoes conversion to the electrophilic species [B20H17NH3]−, which possesses a pair of three-center two-electron bonds and is isoelectronic with [trans-B20H18]2−. An encounter of [B20H17NH3]− with an intracellular protein containing a peptide (PEP) that bears a nucleophile (i.e., NH2) will result in covalent bond formation, attaching TAC to the peptide. The isomer shown is the more clearly indicated product of nucleophilic addition to [B20H17NH3]− (26).