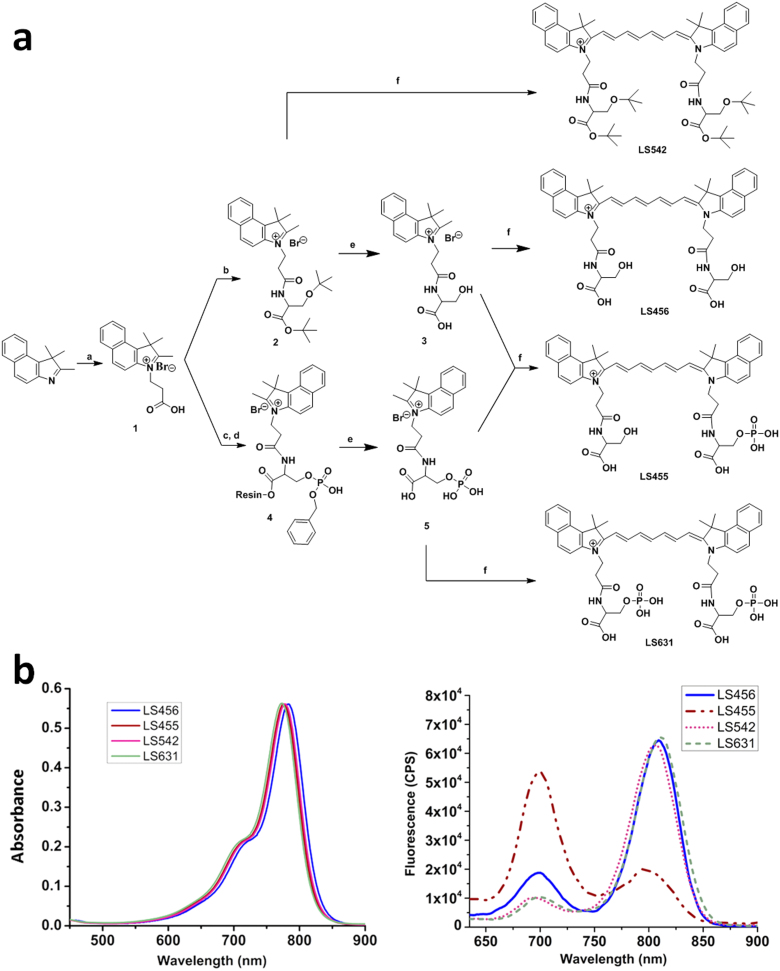
Figure 1. Structures and spectra of molecular reporter probe and controls.
(A) Synthesis of LS456, LS455, LS542, and LS631. Reagents and conditions: (a) 3-Bromopropionic acid in dichlorobenzene, 120°C; (b) DIC (N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide) and HOBT (hydroxybenzotriazole) in DMF (dimethylformamide) and H-Ser(tBu)-OtBu.HCl; (c) Fmoc-Ser[PO(OBzl)OH]OH was loaded onto Br-Wang resin with cesium iodide and DIEA (N,N-diisopropylethylamine); (d) DIC and HOBT in DMF; (e) 95% TFA/5% H2O; (f) N-(5-anilino-2,4-pentadienylidene)aniline hydrochloride, acetic anhydride, DCM, MeOH, and sodium acetate (see the Methods section for details). LS455 is a model of LS456 after phosphorylation. The control LS542 probe has the hydroxyl phosphorylation site of serine blocked with tert-butyl group. (B) Absorption (left) and emission (right) spectra of LS456, LS455, LS542 and LS631 in methanol. Absorbance units were kept below 0.2 for fluorescence measurements. The fluorescence spectrum of LS455 demonstrates the expected spectral shift when a kinase phosphorylates LS456. CPS, photon counts per second.