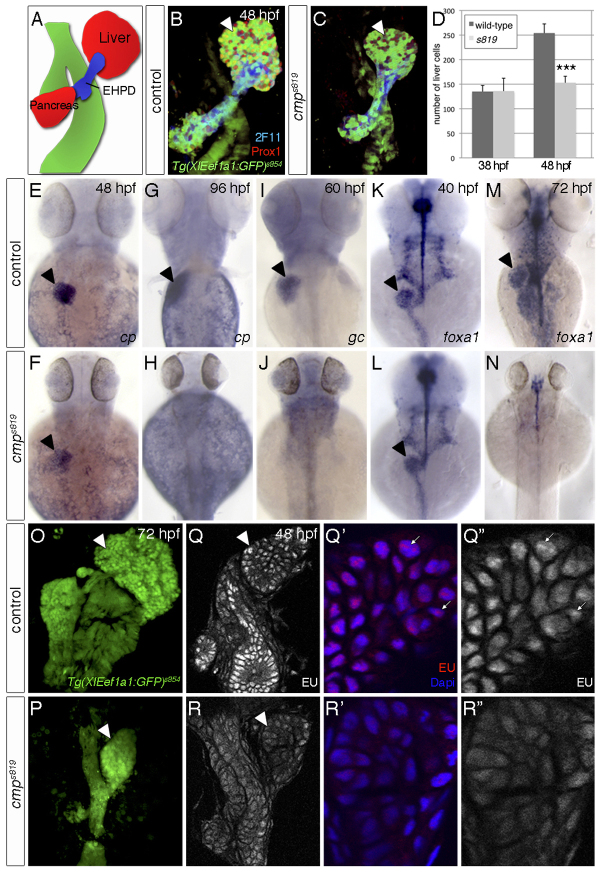
Fig. 1.
cmps819 controls endodermal differentiation and global transcription. (A) Schematic of endodermal organs. (B,C) Confocal projections of endodermal Tg(XlEef1a1:GFP)s854, hepatic and pancreatic Prox1 and 2F11 in the extrahepatopancreatic ducts (EHPD) show liver and pancreas hypoplasia in cmps819 mutants. (D) Prox1-positive hepatoblasts are significantly reduced in cmps819 embryos at 48 hpf; data show mean±s.e.m., ***P=1.2-5. (E-H) At 48 hpf, cp is expressed in cmps819 livers (E,F), but undetectable at 96 hpf (G,H). (I,J) gc expression is absent in cmps819 embryos at 60 hpf. (K-N) foxa1 is expressed throughout the cmps819 endoderm at 40 hpf (K,L) and is absent at 72 hpf, whereas residual foxa1 is detectable in neural tissues (M,N). (O,P) Tg(XIEef1a1:GFP)s854 labels the digestive system in sibling and cmps819 embryos at 72 hpf. (Q-R″) EU incorporation reveals reduced RNA transcription in the digestive system of cmps819 mutants at 48 hpf. Using the same confocal settings, magnifications of representative sections show fewer EU-positive foci (arrows) in cmps819 livers compared with controls. A-C,O-R″ are ventral views; E-N are dorsal views; all show anterior to the top. Arrowheads indicate liver.