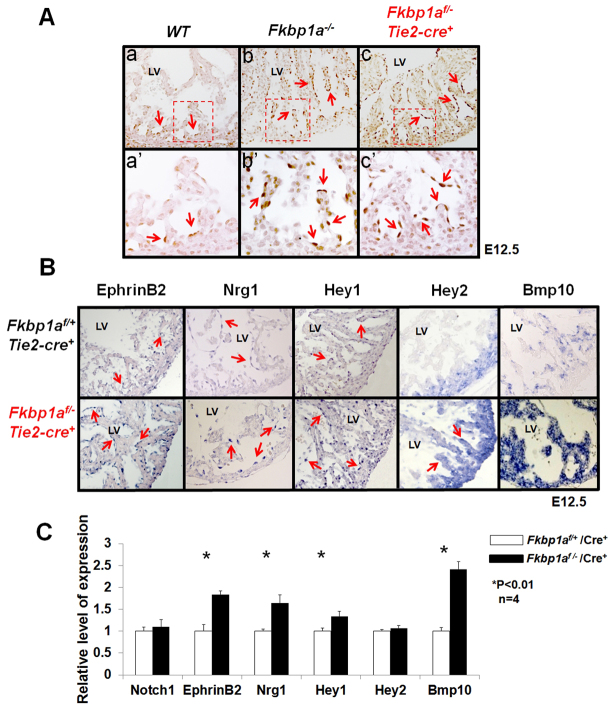
Fig. 5.
Assessment of Notch1-mediated signaling in the developing endocardium of Fkbp1a-deficient and Fkbp1aflox/-:Tie2-cre mouse hearts. (A) Immunohistological analysis using antibody specific to activated Notch1 (N1ICD). In control heart (WT), nuclear N1ICD is mainly located in endothelial cells at the proximal end of trabeculae (arrows in a′). By contrast, N1ICD was found throughout endothelial cells in both Fkbp1a-deficient and Fkbp1aflox/-:Tie2-cre mutant hearts (arrows in b′ and c′). The boxed regions in a-c are magnified in a′-c′. (B) In situ hybridization of downstream targets of Notch1 in Fkbp1aflox/-:Tie2-cre and control hearts at E12.5. Ephrin B2 (Efnb2), neuregulin 1 (Nrg1) and Hey1 are upregulated in endocardial cells in Fkbp1aflox/-:Tie2-cre hearts. Bmp10 is upregulated in both trabecular and compact myocardium. Interestingly, Hey2 expression is upregulated in trabecular myocardium compared with controls. Arrows indicate positive signals. (C) qRT-PCR confirms the expression levels of Notch1, Efnb2, Nrg1, Hey1, Hey2 and Bmp10 in Fkbp1aflox/-:Tie2-cre hearts at E13.5. Interestingly, despite the altered expression pattern, the overall expression level of Hey2 is not altered. Error bars indicate s.e.m. LV, left ventricle.