Figure 1.
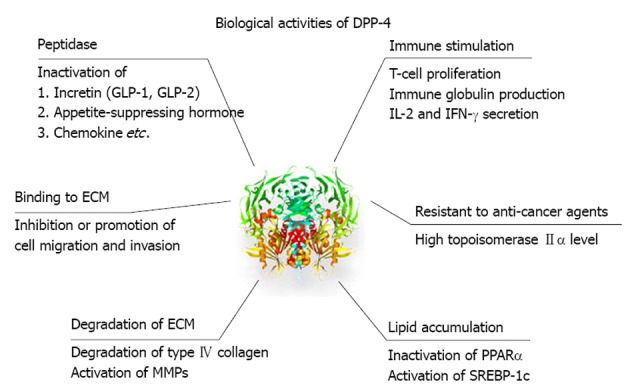
Pleiotropic effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) exerts various effects on metabolism and chemokine through peptidase activity. In addition, DPP-4 is involved in immune stimulation, binding to and degradation of extracellular matrix, and resistant to anti-cancer agents. DPP-4 also directly affects lipid accumulation. GLP: Glucagon-like peptide; ECM: Extracellular matrix; MMPs: Metalloproteinases; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; SREBP: Sterol regulatory element binding protein.
