Figure 5.
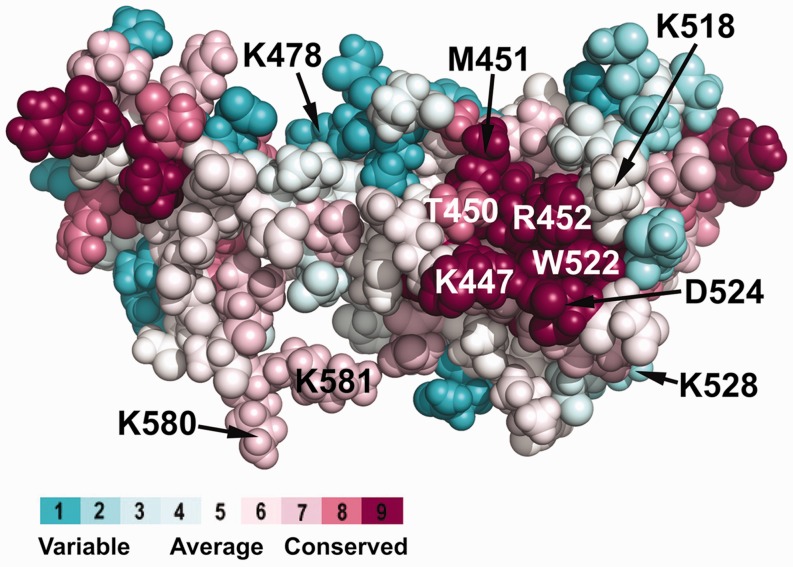
Highly conserved basic and hydrophobic amino acid residues are clustered on the surface of DnaG-C. Using the ConSurf server (55), an alignment of ∼70 bacterial DnaG proteins was projected on the known 3D structure of E. coli DnaG-C [pdb code: 2HAJ (33)]. On the right hand side of the structure, a cluster of highly conserved amino acid residues located on the surface of the N-terminal subdomain of DnaG-C can be observed. Similar to the other characterized SSB-binding sites, it consists of a hydrophobic patch (containing T450, M451 and W522), surrounded by a stretch of basic amino acids (K447, K518 and R452). The colour legend shows the conservation scores of the respective residues. Note that the C-terminal lysine residues K580 and K581 involved in interaction of DnaG-C with DnaB helicase (34) are also labelled.