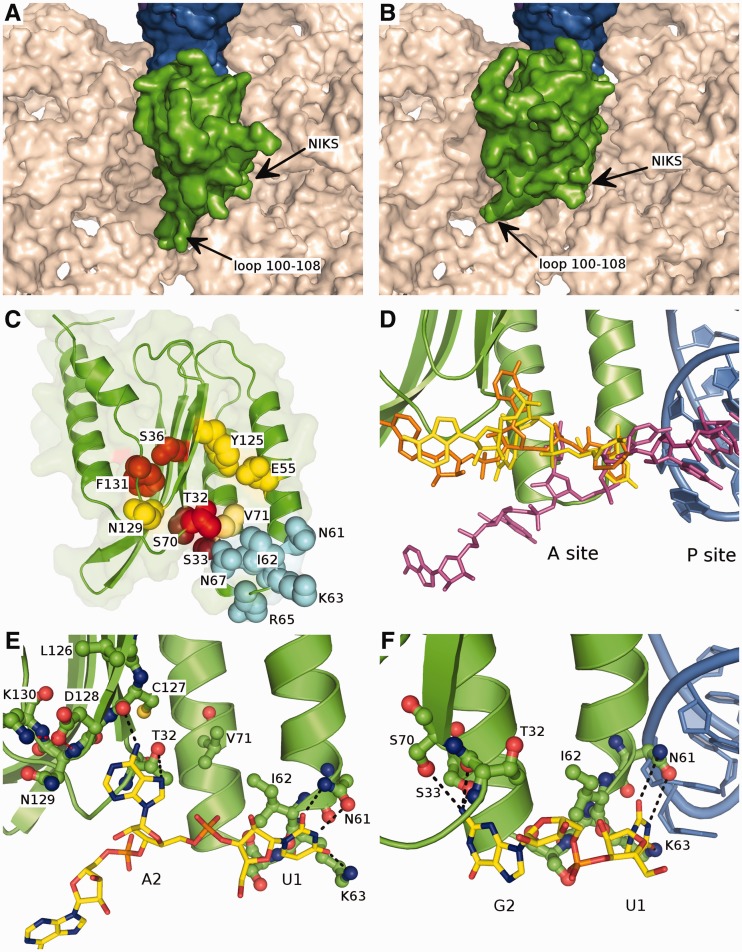
Figure 5.
Modelled orientation of eRF1 at the A site of the ribosome. (A and B) The first and second options of eRF1 N-domain (green) orientation at the ribosomal A site. The surface of 18S rRNA is shown in beige, tRNA in the P site is in blue. (C) The overall structure of the eRF1 N-domain. The amino acid residues important for the stop codon decoding are shown in spheres; the residues involved in the recognition of U1 are coloured in light blue, those important for the decoding of the second nucleotide are coloured in red, and those important for the third nucleotide recognition are coloured in yellow. (D) Comparison of the position of mRNA in the ribosome A site from the cryo-EM structure (56) (purple) and the modelled conformations of the mRNA (UGA and UAA codons are in yellow and orange, respectively) bound to eRF1: the bound mRNA is pulled onto the eRF1 and thus into the ribosome. (E) The proposed mode of binding of the UAR first two nucleotides. Stop codon is shown in yellow, eRF1 N-domain is green, black dotted-lines depict the possible contacts between eRF1 and the stop codon, red dotted lines correspond to the inter-eRF1 contacts. (F) 90° rotation of (E) with the first two nucleotides of UGA codon bound to eRF1, tRNA in the P site is shown in blue.