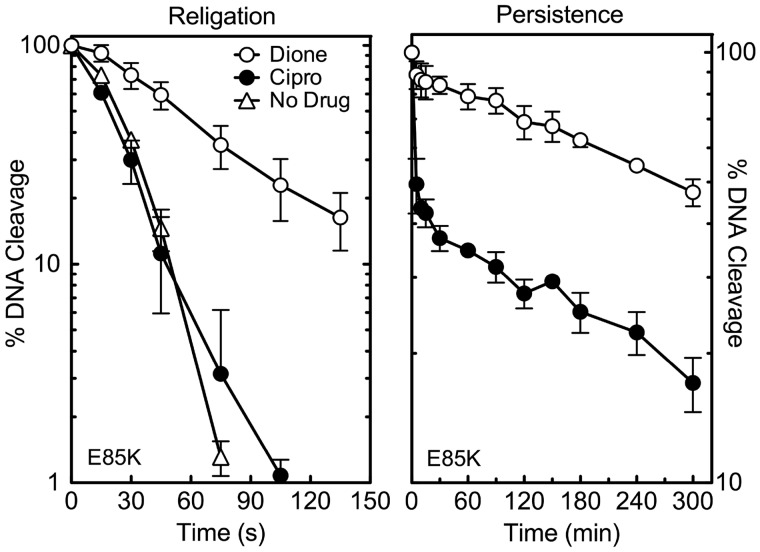
Figure 7.
Effects of ciprofloxacin and 8-methyl-2,4-dione on the DNA religation activity of GrlAE85K topoisomerase IV and the persistence of ternary GrlAE85K topoisomerase IV-drug-DNA cleavage complexes. Results for religation assays carried out in the absence of drugs (No Drug, open triangles) or in the presence of quinolone (ciprofloxacin; Cipro, black circles) or quinazolinedione (8-methyl-2,4-dione; Dione, open circles) are shown on the left. Results for the persistence of ternary cleavage complexes formed in the presence of ciprofloxacin (Cipro, black circles) or 8-methyl-2,4-dione (Dione, open circles) are shown on the right. For persistence assays, initial DNA cleavage-religation reactions were allowed to come to equilibrium and were then diluted 20-fold with DNA cleavage buffer. In both assays, ciprofloxacin was used at 200 µM, and 8-methyl-2,4-dione was used at 20 µM. Levels of DNA cleavage at time zero were set to 100%, and results were quantified by monitoring the loss of double-stranded DNA breaks (FIII linear band) over time. Religation reactions carried out in the absence of drugs replaced Mg2+ with Ca2+ to achieve readily quantifiable levels of DNA cleavage. Rates of religation obtained in the presence of the two metal ions are similar. Representative gels are shown in Supplementary Figure S6. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three or more independent experiments.