Figure 3.
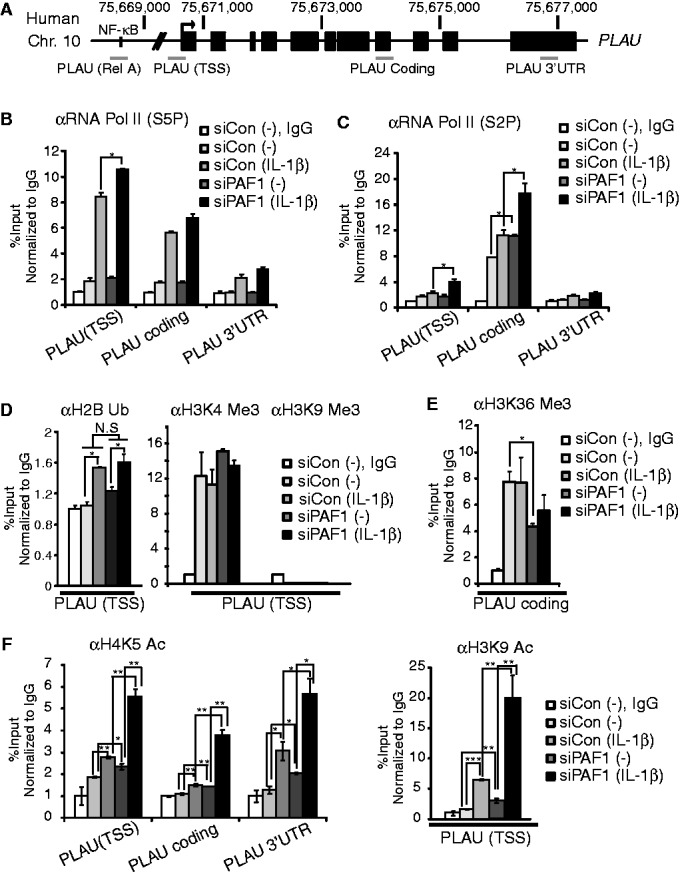
PAF1 deficiency enhances RNA polymerase II progression and histone acetylation at the PLAU locus. (A) Schematic illustration of the PLAU locus and the ChIP primers used in this article. (B–F) ChIP analysis of RNA Pol II with phosphoserine 5 on CTD (B), RNA Pol II with phosphoserine 2 on CTD (C), H2B ubiquitination, H3K4 trimethylation or H3K9 trimethylation (D), H3K36 trimethylation (E) and H4K5 acetylation or H3K9 acetylation (F). HepG2 cells were transfected with control or PAF1 siRNA and stimulated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 0 or 30 min. The PCR amplification was performed using ChIP primers as indicated. The specific ChIP signal at the target locus relative to the intergenic region was calculated and normalized to an IgG negative control. Mean ± SD of two experiments was presented.
