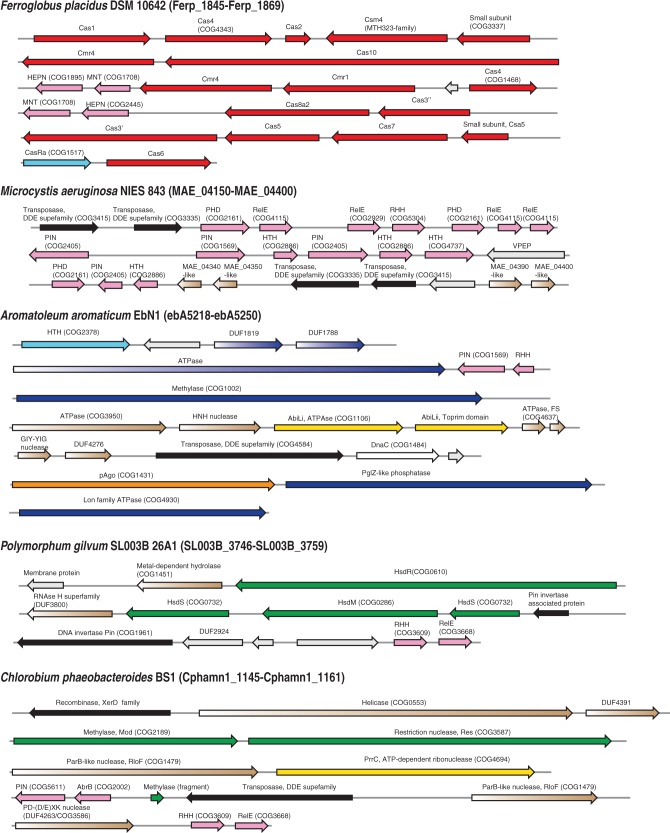
Figure 3.
Examples of defense islands in archaeal and bacterial genomes. The genes are shown by block arrows with the size roughly proportional to the size of the corresponding gene. The genomic position of each region is indicated given in parentheses after the species name in the form of the range of genes denoted using the systematic names for the respective species. Colour coding is the following: pink are components of TA systems, read, components of CRISPR-Cas systems; dark blue, Pgl system; light blue, regulatory components; green, R-M systems; yellow, ABI system; orange, pAgo; brown, components that are spredicted to be involved in defense; grey, unknown protein. The protein family or domains names are provided above the respective arrows; some of these families were recently introduced and described in the course of comparative genomic analysis of defense islands (5); COG or Pfam families are indicated in parentheses. Pgl, Phage Growth Limitation; HTH, helix-turn-helix; RHH, ribbon-helix-helix; GIY-YIG, conserved motif in a nuclease family.