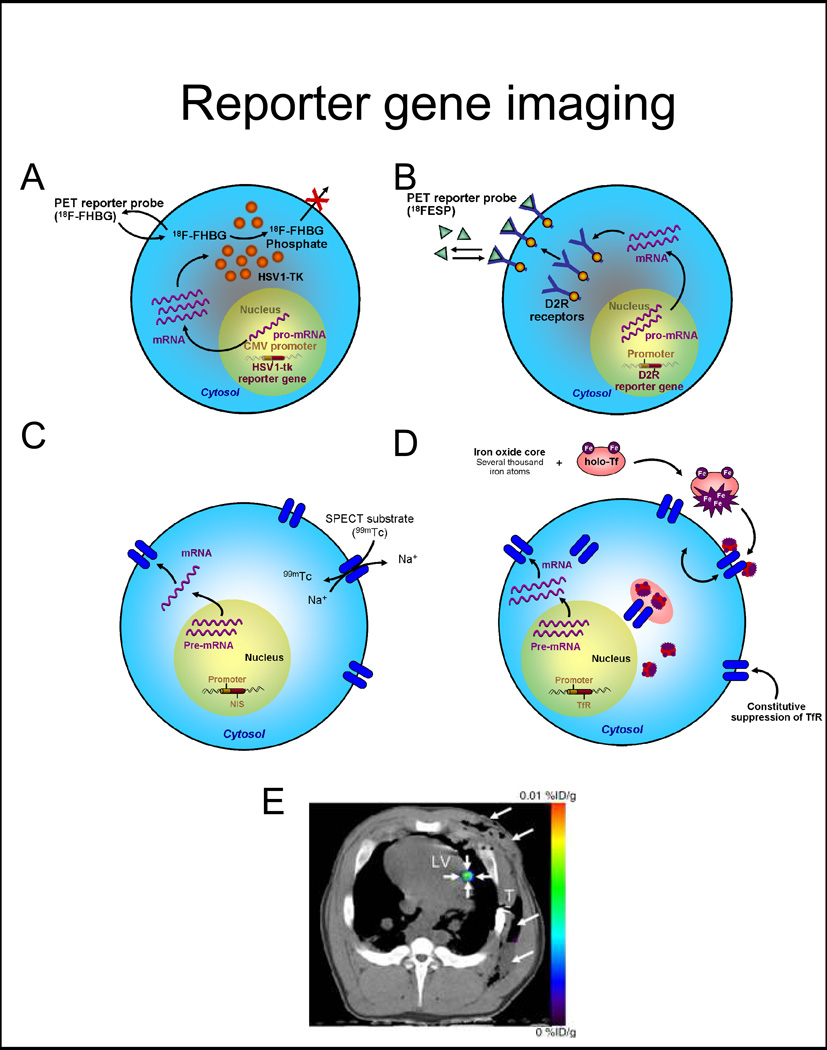
Figure 2. Reporter gene imaging strategies.
A, Enzyme-based PET imaging. 18F-FHBG is a substrate molecular probe that is phosphorylated by the HSV1-tk enzyme resulting in intracellular trapping of the probe in cells expressing the HSV1-tk gene. B, Receptor-based PET imaging. 18F-FESP is a ligand molecular probe interacting with the D2R to result in trapping of the probe in cells expressing the D2R gene. C, Symporter-based SPECT imaging. 99Tc is uptaken by the progenitor cell expressing the NIS reporter gene in exchange for Na+. D, Receptor-based MR imaging. Iron enters the cell through transferrin receptors. The signal detection by MRI is based on the T2* effect (as in direct labeling). E, Representative PET-CT image of 3×107 MSCs, transduced with Ad-CMV-HSV1-sr39tk, and transplanted to the myocardium of swine. 18F-FHBG was administered intravenously and transverse non-enhanced PET-CT imaging was performed after four hours. Small arrows depict the signal at the intramyocardial injection site, while large arrows point to the post-operative changes following delivery.
Abbreviations: 18F-FHBG: 9-[4-[18F]fluoro-3-(hydroxymethyl)butyl]guanine, HSV1-sr39tk: mutant herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase, 18F-FESP: 3-N-(2-[18F]Fluoroethyl)spiperone, D2R: dopamine-2 receptor, NIS: sodium iodide symporter, TfR: transferrin receptor, PET-CT: positron emission tomography-computed tomography. Adapted from Wu et al. J Nucl Cardiol 2004 Jul–Aug 11(4):491–505 and Willmann et al. Radiology 2009; 252:117–127 with permission.