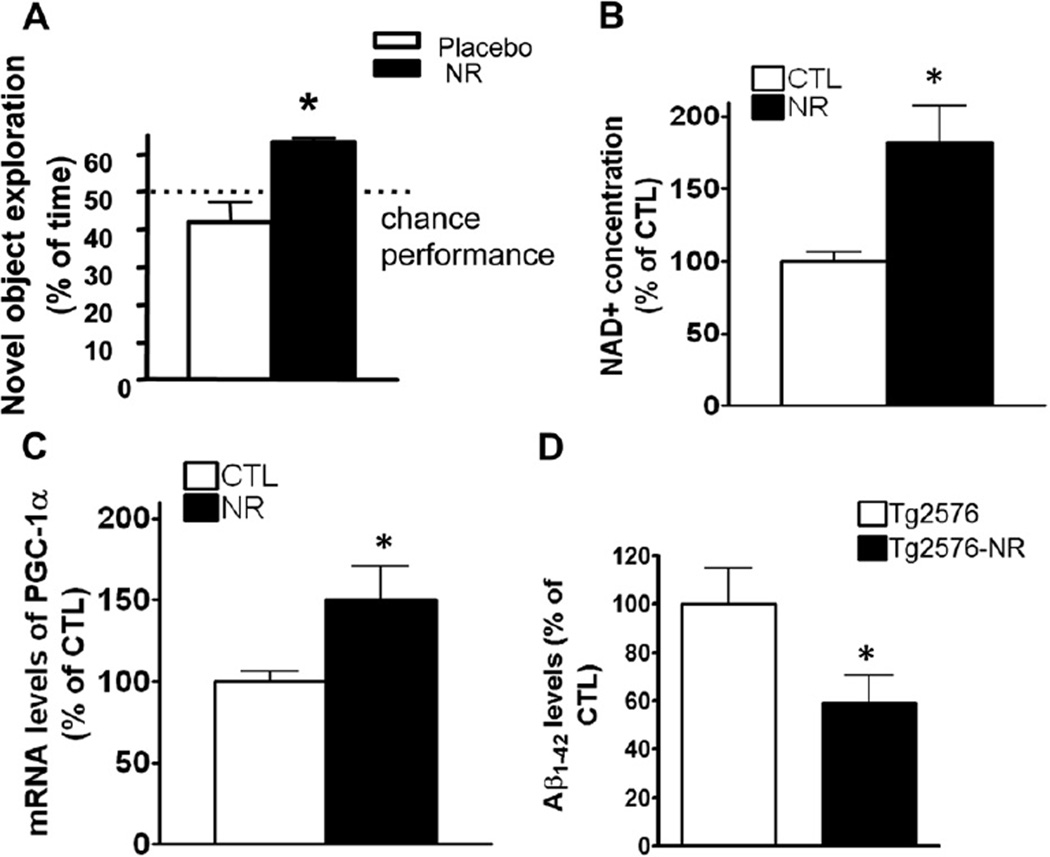
Fig. 1.
NR improves cognitive function in Tg2576 mice via a promotion of NAD+ and PGC-1α levels. (A) Treatment with NR 250 mg/kg/day in Tg2576 mice for 3 months improves cognitive function. Object recognition memory test, performed as described by Bevins and Besheer (2006). Values are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean, n = 10 mice per group. * p < 0.05, 2-tailed Student t test. (B) The NR treatment significantly increased the levels of NAD+ levels measured by NAD/NADH Assay Kit (Abcam). (C) PGC-1α mRNA levels in brain. Values are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean, n = 8 mice per group. * p < 0.05, n = 5 mice per group, 2-tailed Student t test. (D) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed the levels of Aβ1–42 levels in brains treated with NR comparing with placebo-treated brains in Tg2576 mice. n = 8 mice. Abbreviations: Aβ, beta-amyloid; CTL, control; mRNA, messenger RNA; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NR, nicotinamide riboside; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α.