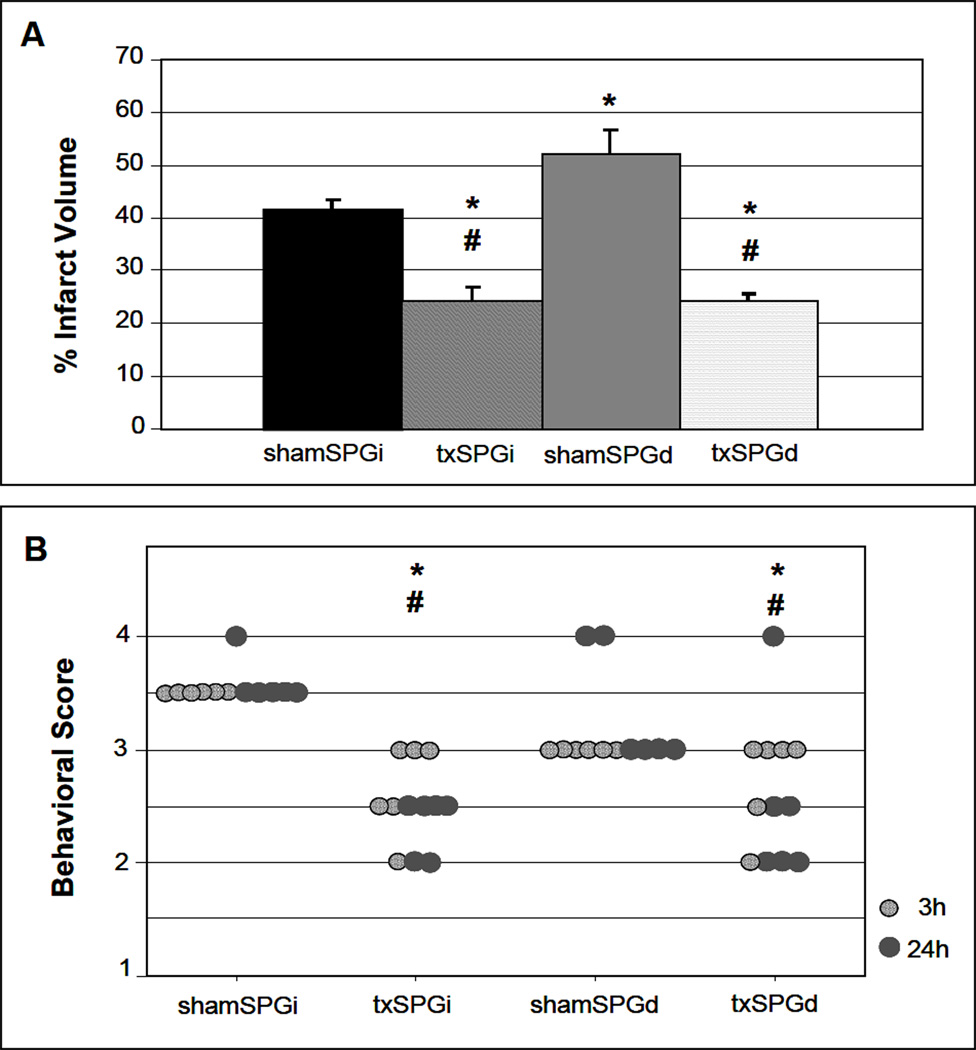
Figure 2.
The effect of VNS on infarct size (A) and neurological deficit (B) after MCA occlusion. (A) VNS is associated with reduced infarct size in both SPGi and SPGd animals. Among sham stimulation animals, the infarct volume was larger in shamSPGd than shamSPGi. ANOVA F(3,20)=22.04, p<0.0001; Student-Newman-Keuls test: * p<0.05 vs. shamSPGi, +p<0.05 vs. shamSPGd. (B) VNS is associated with better functional outcome in both SPGi and SPGd animals 24 h after ischemia. Repeated measures ANOVA: F(3,20)=6.14, p=0.0039; Mann-Whitney U test: * p<0.05 vs. shamSPGi, +p<0.05 vs. shamSPGd.