Figure 2. Association of season-specific 25-(OH)D Z score with the risk for incident myocardial infarction, cancer, hip fracture, or death (composite outcome) among 1621 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study, evaluated using a penalized spline.
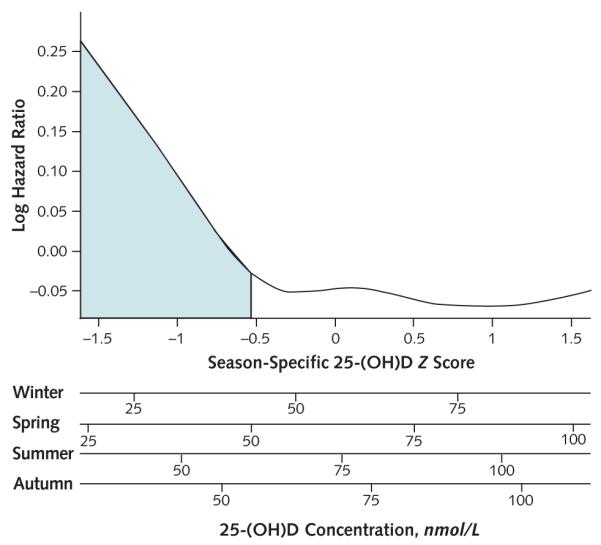
Proportional hazards model adjusts for age, sex, clinical site, body mass index, physical activity, and smoking. The shaded area represents Z score less than −0.54 (29th percentile of the normal distribution), which best discriminated risk for the composite outcome. The x-axis is displayed as season-specific Z score (uppermost x-axis, reflecting the primary method of analysis) and as corresponding season-specific absolute 25-(OH)D concentrations (lower 4 axes). 25-(OH)D = 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
