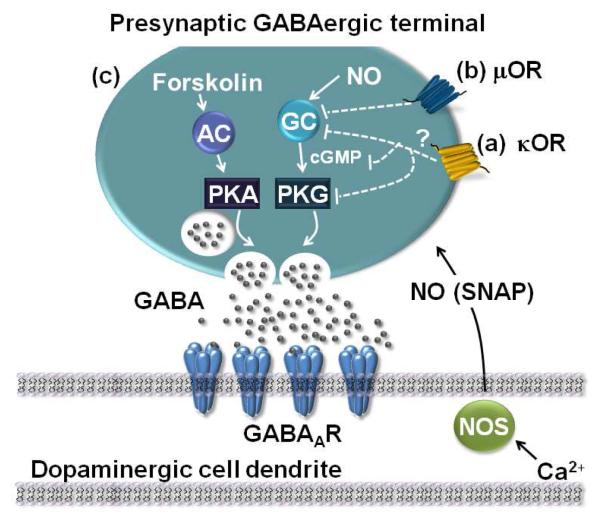
Figure 7. Proposed model of signaling molecules involved in LTPGABA.
(A), an in vivo exposure to stress blocks LTPGABA through activation of kappa opioid receptors (KORs) with subsequent modulation of the NO signaling pathway at a point downstream of NO production. Presynaptic terminals expressing LTPGABA may originate from local interneurons or extrinsic GABAergic afferents. (B), in vivo exposure to morphine alters LTPGABA through activation of μ-opioid receptors (μOR), inhibiting the cGMP pathway at the level of sGC (soluble guanylate cyclase)(Niehaus et al., 2010). (C), Forskolin potentiates GABAergic synapses by activating adenylyl cyclase (AC), which in turn activates the cAMP/PKA pathway. This pathway is unaffected by in vivo manipulations with morphine or stress (Nugent et al., 2009).