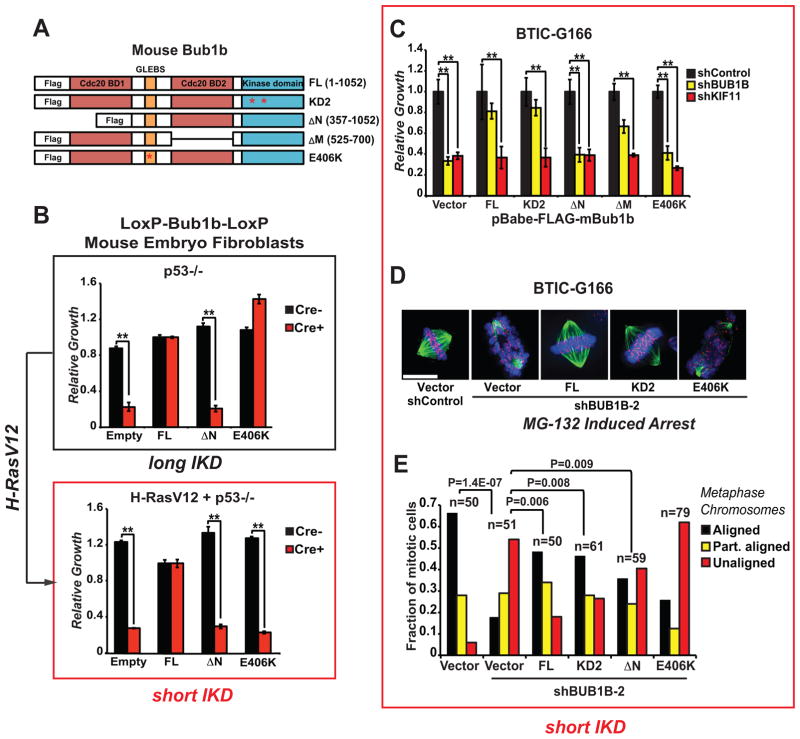
Figure 5. Allelic complementation studies with mouse Bub1b mutants in Bub1b−/− MEFs and BTICs.
(A) The mouse alleles used in these studies were previously published and include: full length; KD2, which harbors two point mutations in the kinase domain (K784>R in the ATP binding domain and K802>R in the catalytic domain); ΔN, which lacks the N-terminal Cdc20-binding domain 1; ΔM, which lacks the C-terminal Cdc20-binding domain 2; and E406K, which creates a point mutation in the GLEBS motif that interferes with kinetochore localization and Bub3 binding.
(B) Viability assessment of complementation studies using p53−/− MEFs with floxed alleles of Bub1b with and without transformation via H-RasV12.
Knockdown of BUB1B in Ras-transformed normal human astrocytes (NHAs) phenocopies BUB1B requirement observed in BTICs with respect to viability. MEFs were transduced with MSCV-GFP-mBub1b constructs, sorted for GFP+, outgrown, transduced with pMSCV-Puro-Cre, selected, and seeded into microtiter growth dishes for proliferation assays.
(C) Viability assessment of complementation studies using BTIC-G166 with shBUB1B (or controls) expressing each of five mBub1b alleles from (A). Assays were performed as in Figure 1C.
(D) & (E) Chromosome alignment after complementation of BUB1B knockdown with mBub1b alleles, as in Figure 4A & 4B. Scale bar indicates 10 microns.