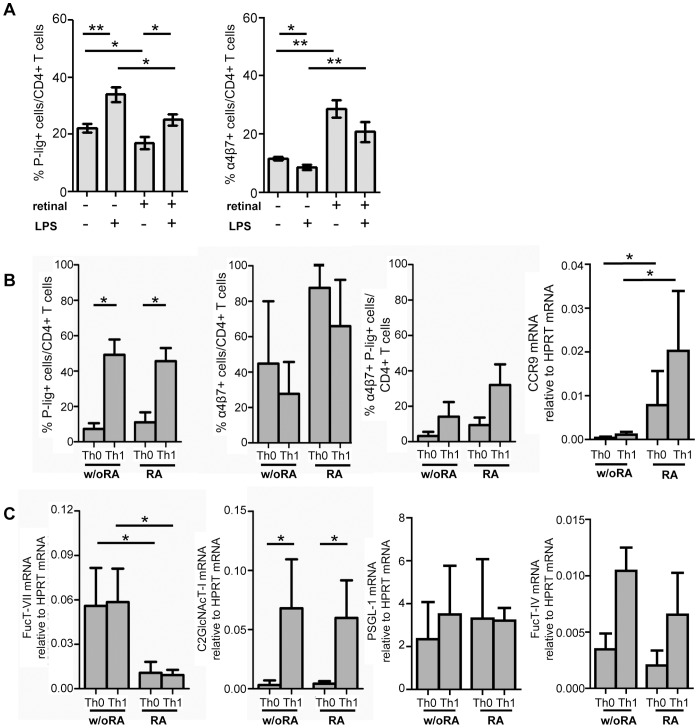
Figure 3. Inflammatory stimuli increase P-lig but reduce α4β7induction on CD4+ T cells even in the presence of RA.
A) Naive OVA-TCRtg CD4+ T cells were activated with OVA323–339 peptide and CD11c+ DCs from MLN in the presence or absence of LPS and presence or absence of 10 nM retinal. Percentage of P-lig+/CD4+ T cells and α4β7+/CD4+ T cells (mean + SD of n = 6 from two independent experiments) was determined on d5 after activation. B) Naive CD4+ T cells were activated by plate bound antiCD3/antiCD28 in the presence or absence of polarizing cytokines and 10 nM retinoic acid. The frequency of P-lig+, α4β7+ as well as double-positive CD4+ T cells was determined on day 4 by FACS while CCR9 expression was determined on mRNA level (mean + SD, n = 4 from four independent experiments). C) FucT-VII and C2GlcNAcT-I mRNA as well as PSGL-1 and FucT-IV mRNA expression were determined on day 4 after activation (mean + SD of four independent experiments). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; Mann Whitney U test (for A–C).