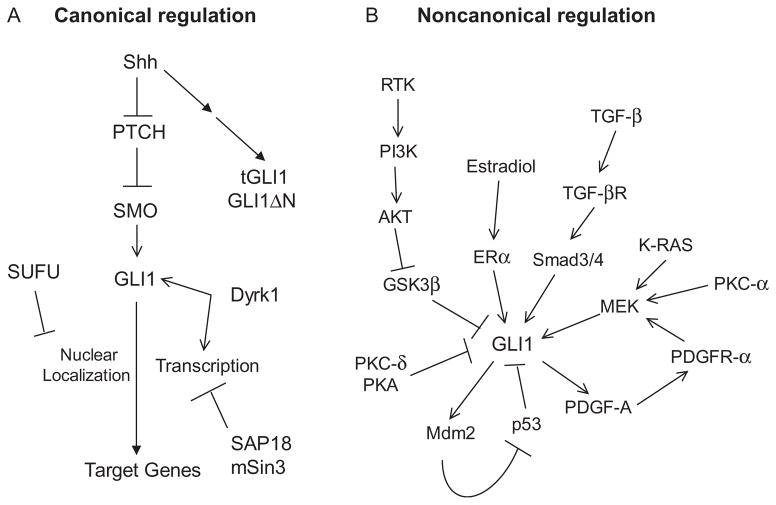
Figure 6.2.
Regulation of GLI1 the isoforms by the canonical and noncanonical pathways. (A) Canonical activation of GLI1 is initiated by Shh, which binds and inhibits PTCH1 relieving PTCH1-mediated suppression of SMO. Derepressed SMO releases GLI1 from SUFU-mediated cytoplasmic sequestration. In turn, GLI1 translocalizes to the nucleus to induce transcription of target genes. Dyrk1 enhances GLI1 activity. Both GLI1ΔN and tGLI1 respond to Shh; however, it is unknown whether they are subjected to the regulation by other components of the Hedgehog pathway. (B) GLI1 can be affected by several noncanonical pathways. Activators of GLI1 include TGF-β, K-Ras, PKC-α, PDGF-A, PI3K-AKT, and estradiol. PKC-δ, PKA, and p53 suppress GLI1. The response of tGLI1 or GLI1ΔN to noncanonical pathway activation is currently unknown.