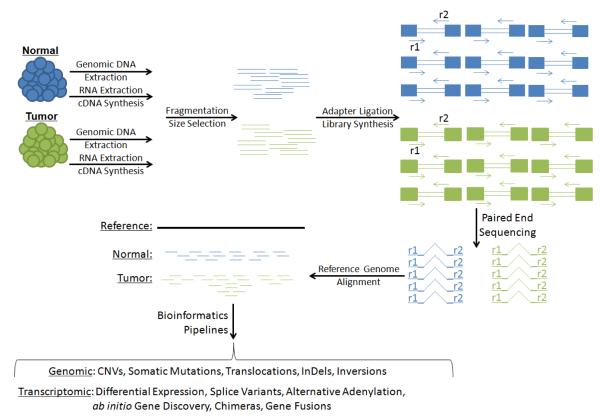
Figure 1. Shotgun Sequencing.
Genomic DNA and cDNA synthesized from RNA are fragmented into a size range compatible with the specifications of massively parallel high-throughput sequencing machines. During repair of fragmented ends, distinct adapters are ligated to each end, permitting paired-end sequencing of DNA fragments. Read pairs are then aligned computationally against a reference genome. Read depth at specific loci can be used to assess genomic copy number or RNA expression of genes. Bioinformatic comparisons of normal, tumor, and reference genomes identify sequence variants associated with disease. Discordant read pairs where the ends of a pair align to separate genomic loci nominate structural genomic rearrangements and expressed chimeras. Evidence of junction spanning read pairs supports ab initio annotation of novel genes in previously unannotated loci.