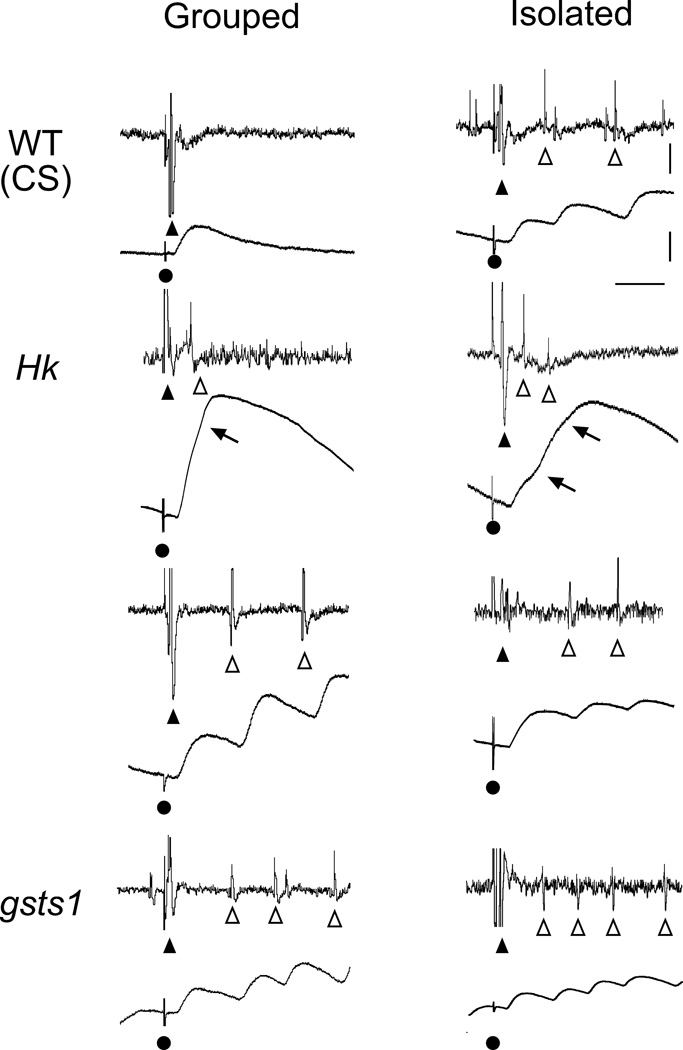
Figure 6.
Increased motor neuron excitability by mutations in Hk and gsts1 and by isolation rearing. During 15-Hz nerve stimulation, group-reared WT displayed only a compound action potential (▲) and a single ejp following nerve stimulation (●). However, isolation-reared WT displayed supernumerary spikes (Δ) coupled with increased ejp amplitudes. Note that Hk and gsts1 mutants displayed supernumerary spikes and giant ejps in both isolation- and group-rearing condition. Two types of supernumerary firing are shown for Hk, one with shorter (< 15 ms) and the other with longer (> 20 ms) inter-spike intervals. They were associated with giant ejps exhibiting notches (arrows) in the rising phase or multiple peaks, respectively. Both types of supernumerary spikes were observed in gsts1 and isolated WT larvae as well.