Abstract
The multinucleate plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum is unusual among eucaryotic cells in that it uses tubulins only in mitotic-spindle microtubules; cytoskeletal, flagellar, and centriolar microtubules are absent in this cell type. We have identified a beta-tubulin cDNA clone, beta 105, which is shown to correspond to the transcript of the betC beta-tubulin locus and to encode beta 2 tubulin, the beta tubulin expressed specifically in the plasmodium and used exclusively in the mitotic spindle. Physarum amoebae utilize tubulins in the cytoskeleton, centrioles, and flagella, in addition to the mitotic spindle. Sequence analysis shows that beta 2 tubulin is only 83% identical to the two beta tubulins expressed in amoebae. This compares with 70 to 83% identity between Physarum beta 2 tubulin and the beta tubulins of yeasts, fungi, alga, trypanosome, fruit fly, chicken, and mouse. On the other hand, Physarum beta 2 tubulin is no more similar to, for example, Aspergillus beta tubulins than it is to those of Drosophila melanogaster or mammals. Several eucaryotes express at least one widely diverged beta tubulin as well as one or more beta tubulins that conform more closely to a consensus beta-tubulin sequence. We suggest that beta-tubulins diverge more when their expression pattern is restricted, especially when this restriction results in their use in fewer functions. This divergence among beta tubulins could have resulted through neutral drift. For example, exclusive use of Physarum beta 2 tubulin in the spindle may have allowed more amino acid substitutions than would be functionally tolerable in the beta tubulins that are utilized in multiple microtubular organelles. Alternatively, restricted use of beta tubulins may allow positive selection to operate more freely to refine beta-tubulin function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkett C. R., Foster K. E., Johnson L., Gull K. Use of monoclonal antibodies to analyse the expression of a multi-tubulin family. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 5;187(2):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burland T. G., Gull K., Schedl T., Boston R. S., Dove W. F. Cell type-dependent expression of tubulins in Physarum. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1852–1859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burland T. G., Schedl T., Gull K., Dove W. F. Genetic analysis of resistance to benzimidazoles in Physarum: differential expression of beta-tubulin genes. Genetics. 1984 Sep;108(1):123–141. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggins M. A., Dove W. F. Distribution of acetylated alpha-tubulin in Physarum polycephalum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):303–309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havercroft J. C., Gull K. Demonstration of different patterns of microtubule organization in Physarum polycephalum myxamoebae and plasmodia using immunofluorescence microscopy. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Toda T., Yanagida M. The NDA3 gene of fission yeast encodes beta-tubulin: a cold-sensitive nda3 mutation reversibly blocks spindle formation and chromosome movement in mitosis. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemphues K. J., Kaufman T. C., Raff R. A., Raff E. C. The testis-specific beta-tubulin subunit in Drosophila melanogaster has multiple functions in spermatogenesis. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., Samson S., Wu J., Hirschberg R., Yarbrough L. R. Tubulin genes of the African trypanosome Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense:nucleotide sequence of a 3.7-kb fragment containing genes for alpha and beta tubulins. Gene. 1985;35(3):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Hernault S. W., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas alpha-tubulin is posttranslationally modified in the flagella during flagellar assembly. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):258–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Gu W., Cowan N. J. Free intermingling of mammalian beta-tubulin isotypes among functionally distinct microtubules. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G. S., Tsang M. L., Smith H., Fidel S., Morris N. R. Aspergillus nidulans beta-tubulin genes are unusually divergent. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro M. J., Cox R. A. Primary structure of an alpha-tubulin gene of Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Porro E. B., Yanofsky C. Cloning and characterization of the gene for beta-tubulin from a benomyl-resistant mutant of Neurospora crassa and its use as a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2452–2461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E. C., Roobol A., Foster K. E., Gull K. Patterns of tubulin isotype synthesis and usage during mitotic spindle morphogenesis in Physarum. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1987;7(3):272–281. doi: 10.1002/cm.970070309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff E. C. Genetics of microtubule systems. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Wilcox M., Paul E. C., Gull K. Identification of tubulin isoforms in the plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum by in vitro microtubule assembly. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;33(1):24–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph J. E., Kimble M., Hoyle H. D., Subler M. A., Raff E. C. Three Drosophila beta-tubulin sequences: a developmentally regulated isoform (beta 3), the testis-specific isoform (beta 2), and an assembly-defective mutation of the testis-specific isoform (B2t8) reveal both an ancient divergence in metazoan isotypes and structural constraints for beta-tubulin function. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2231–2242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Gull K. Flagellar regeneration of the trypanosome Crithidia fasciculata involves post-translational modification of cytoplasmic alpha tubulin. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1182–1185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl T., Burland T. G., Gull K., Dove W. F. Cell cycle regulation of tubulin RNA level, tubulin protein synthesis, and assembly of microtubules in Physarum. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):155–165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
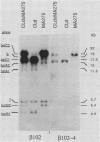
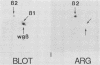
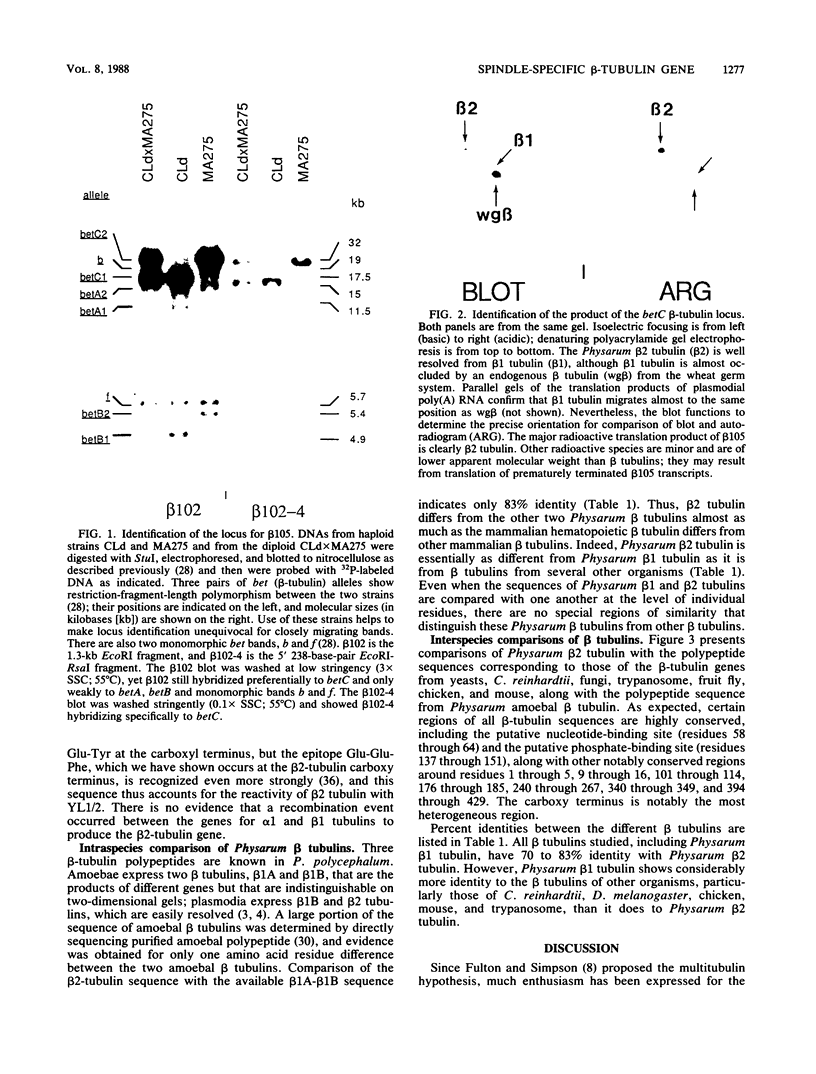
- Schedl T., Owens J., Dove W. F., Burland T. G. Genetics of the tubulin gene families of Physarum. Genetics. 1984 Sep;108(1):143–164. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhofer-Wowra M., Clayton L., Dawson P., Gull K., Little M. Amino-acid sequence data of beta-tubulin from Physarum polycephalum myxamoebae. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):669–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F., Cleveland D. W. Identification of conserved isotype-defining variable region sequences for four vertebrate beta tubulin polypeptide classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F., Cleveland D. W. Sequence of a highly divergent beta tubulin gene reveals regional heterogeneity in the beta tubulin polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1754–1760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F., Lau J. T., Cleveland D. W. Apparent gene conversion between beta-tubulin genes yields multiple regulatory pathways for a single beta-tubulin polypeptide isotype. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2454–2465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Villasante A., Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. The mammalian beta-tubulin repertoire: hematopoietic expression of a novel, heterologous beta-tubulin isotype. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1903–1910. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherbee J. A., May G. S., Gambino J., Morris N. R. Involvement of a particular species of beta-tubulin (beta 3) in conidial development in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):706–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehland J., Schröder H. C., Weber K. Amino acid sequence requirements in the epitope recognized by the alpha-tubulin-specific rat monoclonal antibody YL 1/2. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1295–1300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01965.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngblom J., Schloss J. A., Silflow C. D. The two beta-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii code for identical proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2686–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]