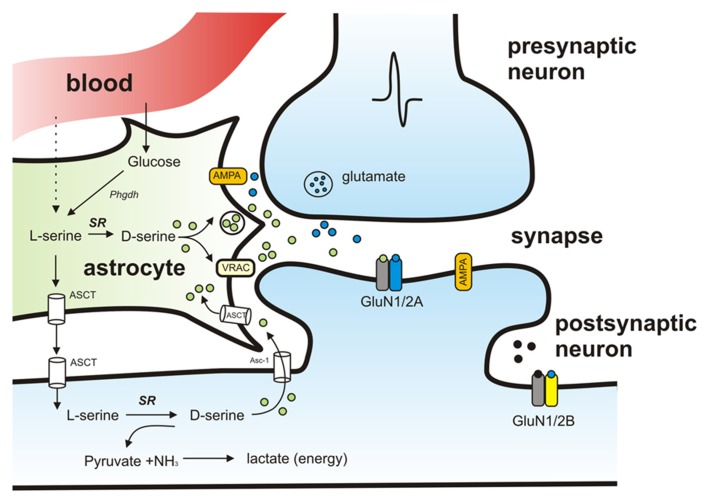
FIGURE 2.
Schematic model of the proposed pathways mediating D-serine synthesis and release. Activation of presynaptic neuron results in release of glutamate that binds to AMPA receptors on neighboring astrocytes and causes release of D-serine. D-serine released from astrocytes binds to synaptic NMDAR-containing GluN2A subunits. Extrasynaptic receptors containing GluN2B preferentially bind glycine instead of D-serine. SR localized in neurons synthesizes D-serine from L-serine. L-serine is shuttled to neurons from astrocytes through amino acid transporters (ASCT). SR is also responsible for the degradation of serine resulting in production of pyruvate and ammonia.