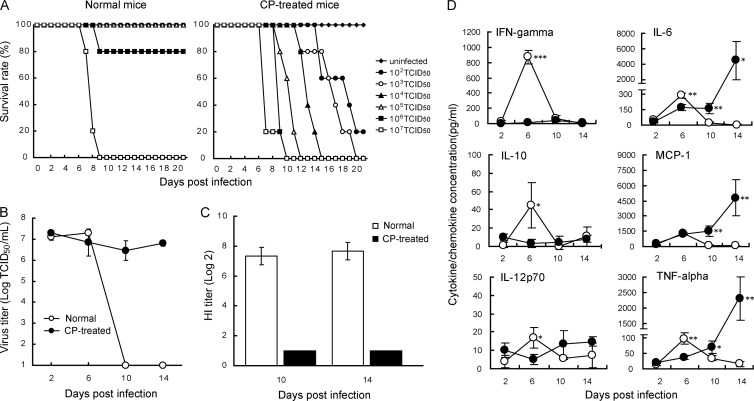
Fig 1.
Effects of cyclophosphamide on survival, replication of influenza virus in lungs, and production of anti-HA antibodies in mice infected with pandemic influenza virus A/Osaka/129/2009 (A/H1N1pdm). BALB/c mice were treated intraperitoneally with 100 mg/kg of cyclophosphamide on days −1, +3, +7, +11, +15, and +19 after virus infection. (A) The numbers of live and dead mice were monitored for 21 days. (B) Viral titers in lung samples collected on indicated days after virus inoculation are indicated as means ± SD for three animals. (C) Sera were collected on indicated days after infection. Diluted sera were incubated with 4 HA units of virus antigen for HI tests. HI titers were expressed as reciprocals of the highest dilution that completely inhibited hemagglutination and are indicated as means ± SD for three animals. (D) Levels of cytokine and chemokine production in lungs collected on indicated days were measured by the bead array assay and are indicated as means ± SD for three animals. Levels of IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-6, and TNF-α secretion were significantly increased on day 6 p.i. in normal mice (open circles) compared with those in CP-treated mice (filled circles). Levels of IL-6, MCP-1, and TNF-α secretion on days 10 and 14 p.i. in CP-treated mice were significantly higher than those in normal mice (*, P < 0.05: **, P < 0.01: ***, P < 0.001).