Fig 6.
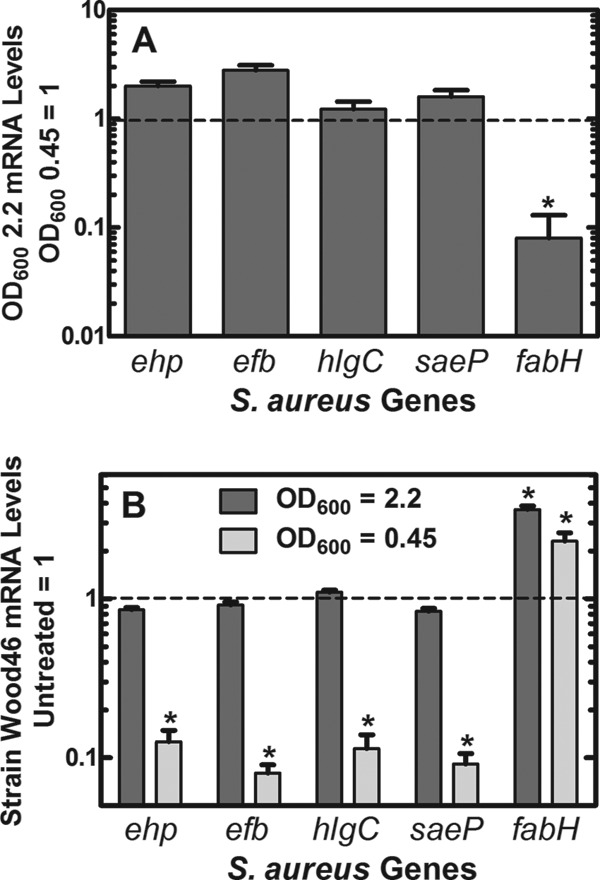
Growth rate dependence of AFN-1252 on virulence factor and fabH mRNA levels. Strain Wood46 was subjected to treatment with AFN-1252 (50 ng/ml) for 15 min either during the logarithmic phase of growth (OD600, 0.45) or after growth slowed as the cells began to enter stationary phase (OD600, 2.2). Transcript abundance in triplicate samples was measured in triplicate by qRT-PCR using gmk as the calibrator. (A) mRNA levels detected at an OD600 of 0.45 were set to 1.0 and compared to the same measurements at an OD600 of 2.2. fabH mRNA was significantly decreased in the samples at the OD600 of 2.2 (*, P < 0.05). mRNA levels for the 4 virulence factors were either unchanged (hlgC) or modestly elevated (∼2-fold) with ehp, efb, and saeP. (B) mRNA levels before AFN-1252 treatment were normalized to 1, and the changes in virulence factor and fabH mRNAs triggered by AFN-1252 are plotted. There was no significant difference between virulence gene expression in cells treated with AFN-1252 at an OD600 of 2.2, but all 4 virulence factors were decreased by about an order of magnitude in cells treated with AFN-1252 at an OD600 of 0.45 (*, P < 0.05). fabH mRNAs were significantly increased in response to AFN-1252 under both experimental conditions (*, P < 0.05). Significance between treated and untreated samples was calculated using the Student t test, and error bars indicate standard deviations.
