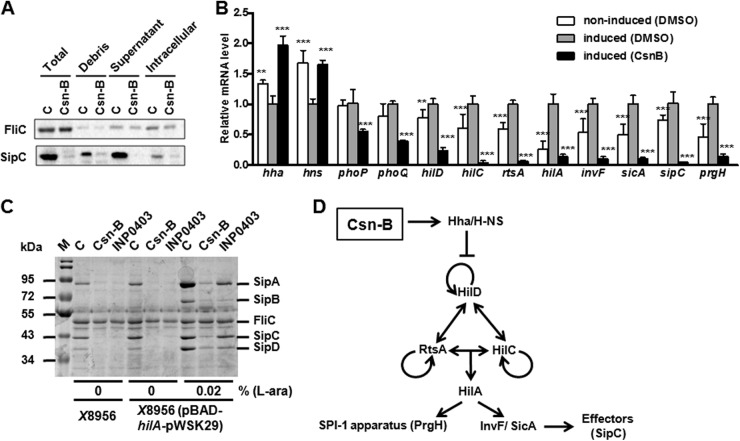
Fig 3.
Csn-B inhibited SPI-1 effectors through the Hha–H-NS regulatory pathway. (A) Effects of Csn-B at a final concentration of 100 μM on SipC in different culture fractions were analyzed by Western blotting. Total, supernatant of bacterial culture after ultrasonic treatment, i.e., supernatant fraction and cytoplasmic fraction; Debris, cell debris of bacteria after ultrasonic treatment; Supernatant, culture supernatant; Intracellular, intracellular fraction of bacterial culture; C, DMSO control. (B) Effect of Csn-B on relative mRNA levels of the SPI-1 regulatory factors, effector gene, and apparatus protein gene. RNA was extracted from bacteria treated with Csn-B at a final concentration of 100 μM or by the same volume of DMSO under an SPI-1-induced condition in vitro or from bacteria treated with the same volume of DMSO under a noninduced condition. The y axis represents the relative transcriptional level of each gene (real-time qPCR) by the relative quantification method. Significant differences: **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. The P value was calculated by comparing the value for the DMSO control under an induced condition. (C) Effect of Csn-B on the secretion of SPI-1 effectors in the HilA-overexpressing strain. S. enterica serovar Typhimurium χ8956 or strain χ8956 carrying plasmid pBAD-hilA-pWSK29 was cultured in LB broth at 25°C overnight; then the cultures were diluted 10 times in LB broth or LB broth supplemented with l-arabinose (0.02%) and ampicillin (100 μg/ml). The diluted cultures were incubated with Csn-B or INP0403 at a final concentration of 100 μM at 37°C for 4 h. The proteins isolated from culture supernatants were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. M, Marker; C, DMSO control. (D) Regulatory pathway of Csn-B on SPI-1. Arrows indicate transcriptional activation. Blunt lines indicate transcriptional inhibition.