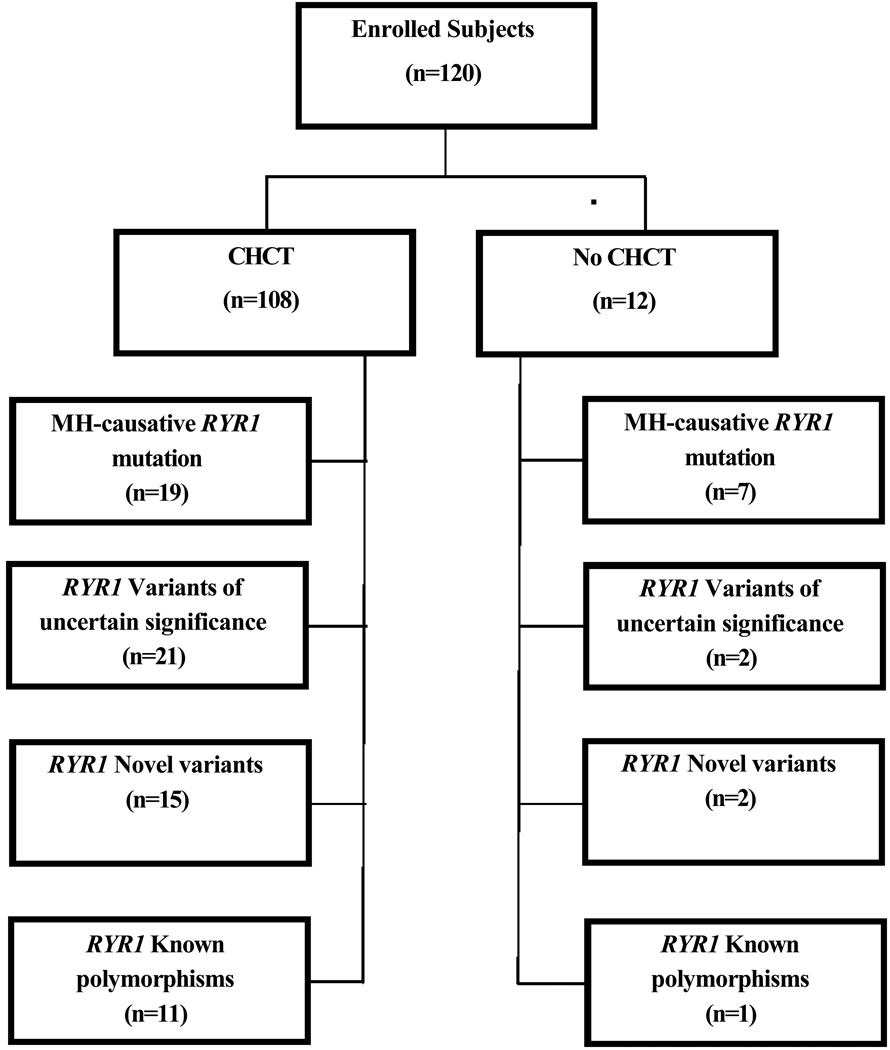
Figure 1.
This flow chart illustrates the outcomes of DNA sequencing for subjects with and without prior caffeine-halothane contracture test (CHCT). A variant of uncertain significance (VUS) is a variant that has been previously reported, but it is not yet proven to be malignant hyperthermia (MH)-causative. A novel variant is a variant that has not been previously reported, and it has not been proven to be MH-causative. A polymorphism is a change in the amino acid sequence of the gene that has been found at least once in 100 normal subjects and is not expected to be pathogenic. The numbers in parentheses are the numbers of subjects found to have this type of change in RYR1.
Two novel variants in the ryanodine receptor type one gene (RYR1) were found in one subject. A novel variant and a VUS in RYR1 were found in one subject. Two different VUS were found in 2 subjects. A VUS and a polymorphism were found in one subject. A novel variant and a polymorphism in RYR1 were found in another subject. One subject had 2 polymorphisms in RYR1. In summary, there were 7 subjects who had 2 different variants when polymorphisms in RYR1 are included in this count. Thus, the sum of the numbers in the sub-boxes is 7 more than the number of subjects in this study reported to have mutations, VUS, novel variants and/or polymorphisms. (see Table 4 and the Web Supplement)