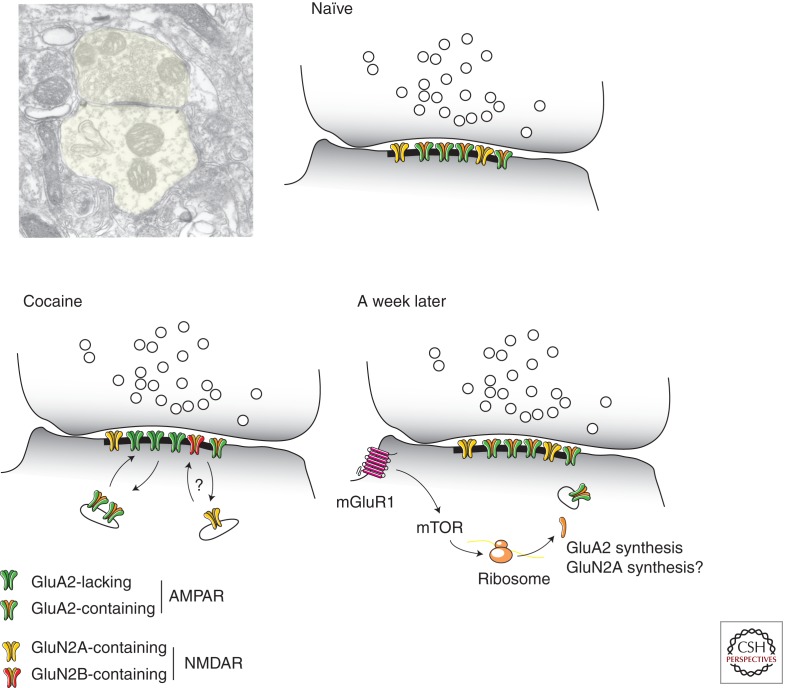
Figure 2.
Receptor subunit redistribution and reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic plasticity in DA neurons. Synapses between glutamatergic afferents and dendrites of VTA dopamine neurons are aspiny. (Top left panel, Electron microscopy picture, courtesy of Rafael Lujan.) Baseline transmission is mediated by GluA2-containing AMPARs and GluN2A-dominated NMDARs. After cocaine exposure GluA2-lacking AMPARs are inserted and NMDARs have a high content of GluN2B (actual exchange of receptors likely, but has not been directly shown). With strong activity, perisynaptic mGluR1s are activated, which through mTOR synthetize new GluA2 subunits. Whether NMDARs are also affected by mGluR1 signaling remains to be investigated.