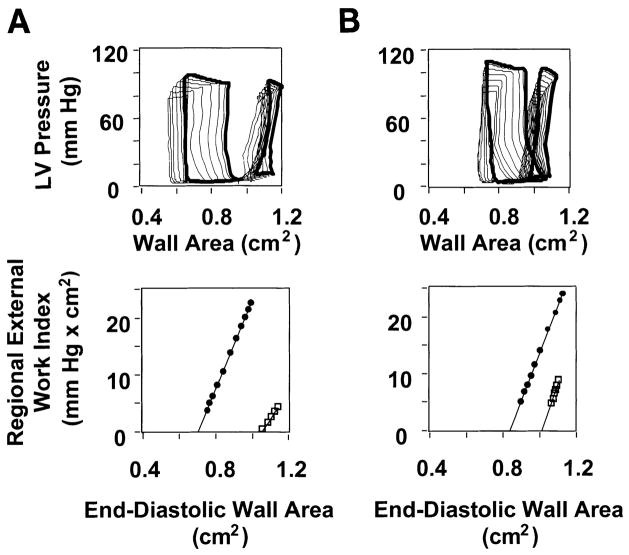
Fig. 5.
Typical ischemic zone LV pressure vs. wall area loops in control and GIK-treated pigs. A and B, top: LV pressure vs. wall area loops were obtained during 10-s occlusion of the venae cavae under baseline conditions (large loops) and after 90 min reperfusion after 90 min ischemia (small loops). Data from a pig in the control group are shown in A, and data from a pig in the GIK group are shown in B. In each example, a loop recorded under steady-state conditions (i.e., before occlusion of the venae cavae) is shown in bold, while loops recorded during occlusion of the venae cavae are shown as light lines. Both pigs exhibit contractile dysfunction after reperfusion, manifest by reduced loop area (an index of regional external work) compared with baseline. However, the recovery of loop area after reperfusion is greater in the GIK-treated pig. A and B, bottom: preload-recruitable stroke work (PRSW) relations derived from data in top by plotting the area of each loop against its corresponding end-diastolic wall area under baseline conditions (●) and after 90 min reperfusion after 90 min ischemia (□). Top point of each PRSW relation indicates steady-state condition, corresponding to the bold loops in top. Data demonstrate that recovery of regional external work is greater in the GIK-treated pig than in the untreated (control group) pig.