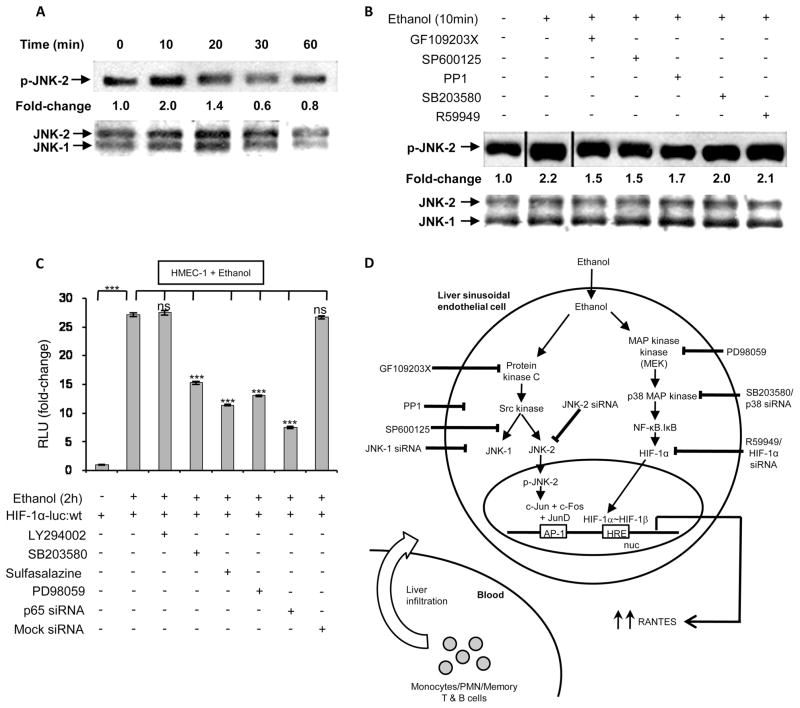
FIGURE 7.
Ethanol-induced cellular signaling leading to RANTES expression involves activation of JNK-2, NF-κB, and HIF-1α. A, Time course of JNK-2 phosphorylation (p-JNK-2) in nuclear extracts from ethanol-treated HMEC-1 cells. The data was normalized to unphosphorylated JNK as a loading control. B, Ethanol-mediated JNK-2 phosphorylation in nuclear extracts of HMEC-1 preincubated with the inhibitors GF109203X, SP600125, PP1, SB203580, or R59949 for 30 min before ethanol treatment. The data are representative of three independent experiments. C, Ethanol augments the interaction of NF-κB proteins with the HIF-1α promoter. HMEC-1 cells were transfected with a HIF-1α luciferase (luc) promoter construct. Where indicated, cells were preincubated with the inhibitors LY294002, SB203580, sulfasalazine, or PD98059 for 30 min before ethanol treatment for 2 h. Luciferase assay data are expressed as fold change and have been normalized as described above. The data represent duplicate assays from three independent experiments (means ± SD). D, Illustration of the ethanol-mediated signaling pathway showing that ethanol metabolism leads to activation of two independent signaling pathways. In one pathway, activation of AP-1 via PKC, Src kinase, and JNK-2 leads to up-regulation of RANTES. This involves an AP-1 complex consisting of c-Jun, c-Fos, and JunD, but not JunB. The second pathway involves activation of HIF-1α via crosstalk with NF-κB, the latter involving activation of MEK. The activation of HIF-1α leads to HRE-binding in the RANTES promoter followed by increased gene transcription. We suggest that ethanol-mediated RANTES generated from LSECs augments the infiltration of monocytes/polymorphonuclear neutrophils and T and B cells from circulation into the liver, contributing to inflammation.