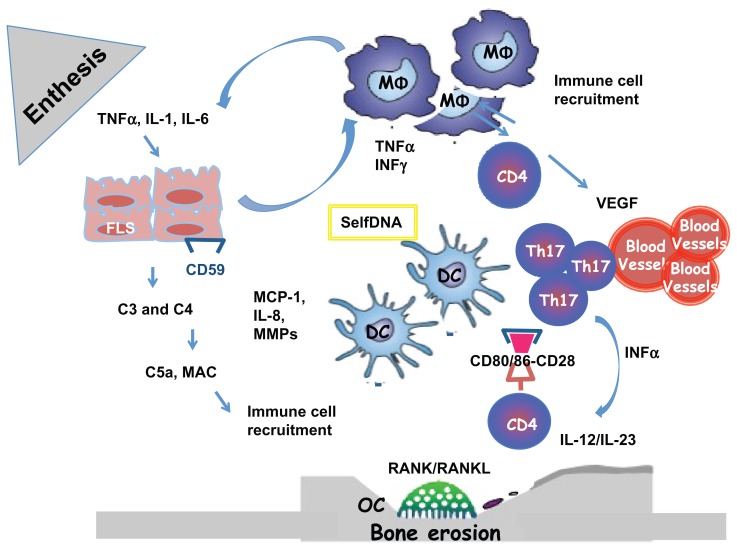
Figure 1.
Enthesal and Joint pathology in Psoriatic Arthritis. The origin of Inflammation in the enthesal complex in PsA is multifactorial. When stimulated by stress, infections and trauma (Koebner phenomenon), in a genetic background, fibroblast-like synoviocytes express selfDNA or/ and secrete inflammatory cytokines and MMPs. They produce complement system factors as C3 and C4 and express less CD59 during inflammation, who is an inhibitor of complement system activation. The activation of the complement system lead to the release of C5a and production of MAC with the lysis of cells and recruitment of immune cells. FLS secrete MCP-1 and IL-8 necessary for recruitment and activation of MΦ. Polyclonal activation of CD4+Tcells and Th17 is the consequence of the immunological synapse with DC linked to the binding with CD80/86 and CD28. When activate CD4+ Tcells produce: RANKL with activation of OC with the consequence of bone erosions and VEGF with the activation of endothelial cells and the formation of HEV
Abbreviations: PsA (Psoriatic Arthritis); FLS (fibroblast-like synoviocytes); TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor); MMP (Matrix metalloproteinases); MCP-1 (monocyte chemotactic protein-1); OC (Osteoclast); MΦ, (monocytes/macrophages); RANK/RANKL (Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B/ ligand); MAC (membrane attack complex); VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor); Th17 (T helper 17); DC (dendritic cell); CD (cluster differentiation).