Figure 4.
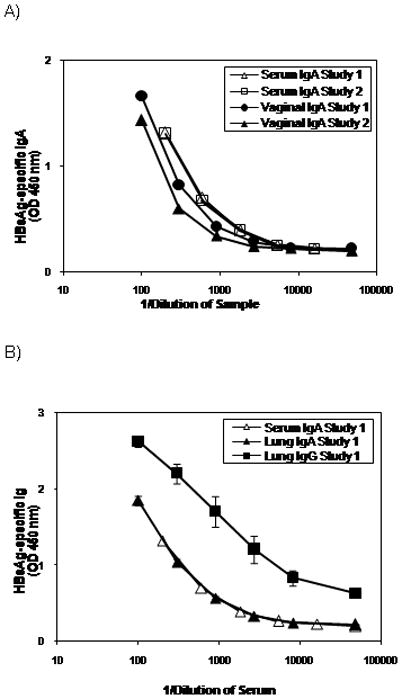
Heterologous immunization induces mucosal IgA and IgG responses. Groups of 6 female Balb/c mice were immunized i.m. on weeks 0 and 4 with 100μg of HBsAg-DNA and i.n. on week 8 with 15μg of HBsAg-liposomes. Serum and vaginal wash samples were collected on week 12, and lung washes were collected on week 14. A, Serum and vaginal IgA responses from two independent experiments. Results show the HBsAg-specific IgA levels determined using a five-layer sandwich ELISA assay. The results are from sample pools using equal volumes of serum or vaginal washes from six mice per group. Negligible (< 2 SD from levels in naïve mice) HBsAg-specific IgA was detected from the following treatment groups: (1) mice that received DNA immunization alone, (2) mice that received HBsAg-liposome alone, and (3) mice that received DNA immunization followed by HBsAg-liposome delivered i.m.(data not shown). B, HBsAg-specific IgA and IgG from the lungs. Results show the HBsAg-specific IgA and IgG levels determined using a five-layer sandwich ELISA assays. Results shown are the mean ± SEM from six mice per group. The serum IgA levels are shown again in this panel for reference.
