Figure 6.
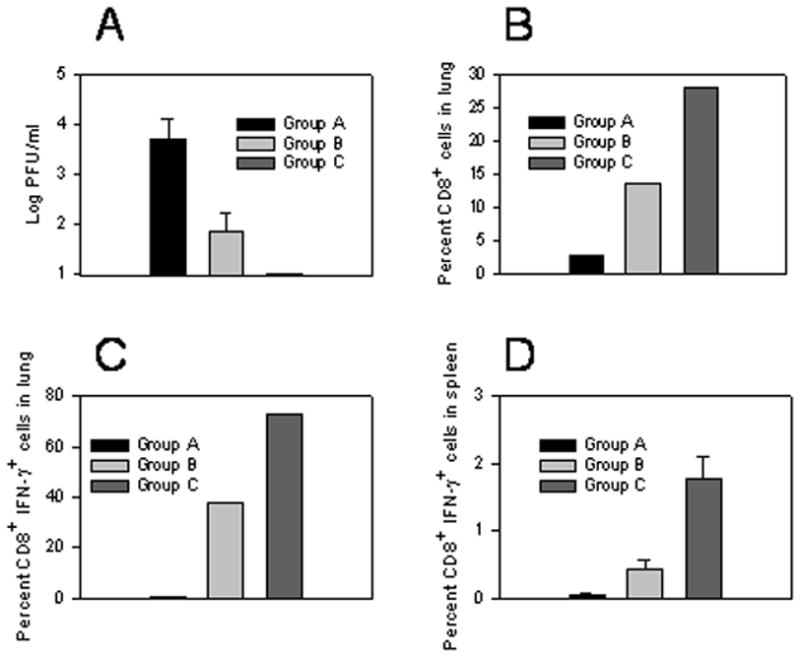
Heterologous immunization induces protective immune responses and high frequencies of CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells. Groups of 5 female Balb/c mice were either left untreated (Group A), were immunized with HBsAg-DNA + empty liposomes (Group B) or were immunized with HBsAg-DNA+HBsAg-liposomes (Group C) using the long immunization protocol. 2 weeks after the last immunization, mice were infected intranasally with 2×105 PFU of vHBs4. 5 days after infection, lungs from 4 mice per group were harvested for determination of viral titers (A), while the final lung was analyzed for total frequency of CD8+ T cells in the mononuclear population (B) and frequency of antigen-specific CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells (C). Individual spleens (4/group +/− SEM) were also analyzed for antigen-specific CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells (D, A vs. B: p=0.01; A vs. C: p=0.0005; B vs. C: p<0.004). All analyses were performed as described in the Materials and Methods. For C and D, cells incubated without peptide showed less than 0.1% positive staining for IFN-γ within the CD8 population (data not shown).
