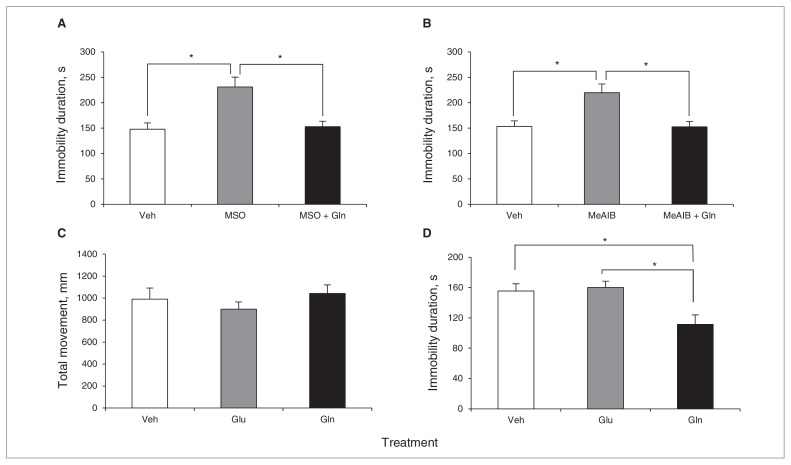
Fig. 5.
Effects of glutamine (Gln) administration on immobility of mice infused with methionine sulfoximine (MSO) or α-methyl-amino-isobutyric acid (MeAIB) and control mice. Glutamine (0.2 μmol) reversed the duration of immobility induced by MSO (0.1 μmol, A, F2,12 = 8.527, p = 0.005; Dunnett post hoc tests were performed to compare MSO and the other 2 groups) and MeAIB (0.07 μmol, B, F2,12 = 8.294, p < 0.005; Dunnett post hoc tests were performed to compare MeAIB and the other 2 groups). Glutamate (Glu; 0.2 μmol) and Gln (0.2 μmol) had no influence on the locomotor activity of control mice (C, F2,12 = 0.758, p = 0.49). Glutamine reduced the duration of immobility of control mice, but Glu did not (D, F2,12 = 6.670, p = 0.011; Dunnett post hoc tests were performed to compare Gln and the other 2 groups). The open field test and forced swim test were performed using the same animals in 1 day. Data are presented as means and standard errors of the mean. *p < 0.05, n = 5 per group.