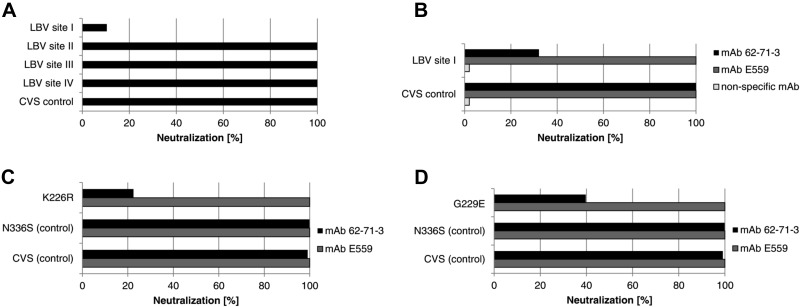
Figure 6.
Mutational analysis of the RV glycoprotein using the E. coli-derived 62-71-3 scFv and the plant-derived 62-71-3 IgG. A) Phage-displayed 62-71-3 scFv was tested against a set of pseudotype viruses containing either the CVS11 wild-type glycoprotein (CVS control) or mutated CVS11 glycoproteins containing the antigenic sites of LBV (LBV site I/II/III/IV) within the CVS backbone. B) Plant-derived mAbs 62-71-3 and E559 and a nonspecific mAb were tested regarding their neutralization of pseudotype viruses containing either the CVS11 wild-type glycoprotein or a mutated CVS11 glycoprotein containing LBV antigenic site I (aa 226–231). C) Role of antigenic site I residue K226 was investigated by testing the plant-derived mAbs 62-71-3 and E559 regarding their neutralization of pseudotypes containing glycoproteins with a K226R mutation. Controls included pseudotypes containing the CVS11 wild-type glycoprotein (CVS control) or containing the CVS glycoprotein containing a nonspecific mutation within antigenic site III (N336S control). D) Neutralization of a site I mutant containing a G229E mutation by mAbs 62-71-3 and E559.