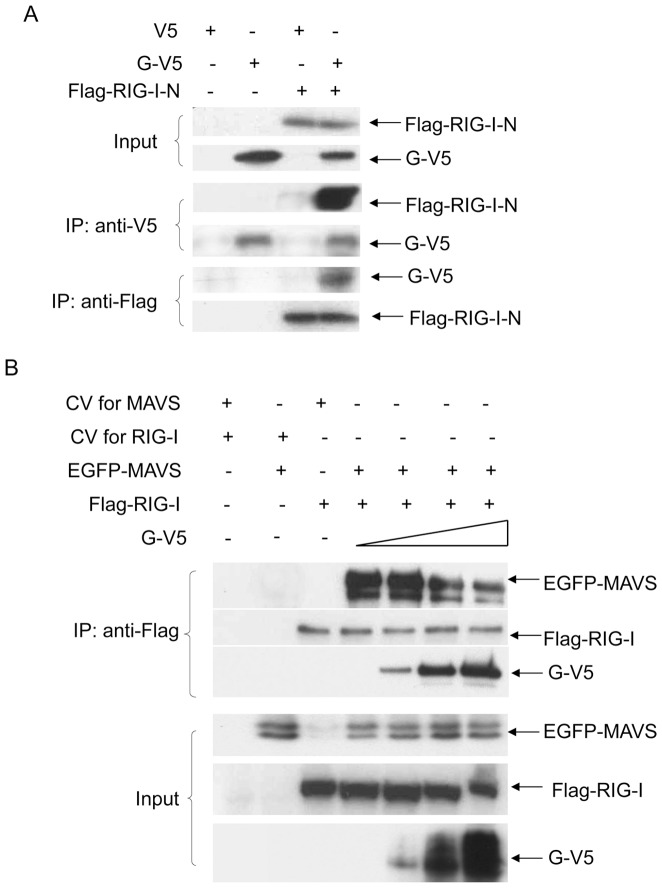
Figure 1. G protein blocks the interaction between RIG-I and MAVS.
(A) 293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Flag-tagged RIG-I-N and V5-tagged G or their control vectors. Total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 antibody followed by Western blot using anti-Flag antibody to detect RIG-I-N. Reverse immunoprecipitation was also done, where RIG-I-N was immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag antibody and G protein was then detected using anti-V5 antibody. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot to determine levels of hMPV G and RIG-I-N expression. (B) 293 cells were transfected with a fixed amount of plasmids encoding Flag-tagged RIG-I and EGFP-tagged MAVS, or their control vectors, and increasing concentrations of a plasmid expressing V5-tagged G. Total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody to pull down RIG-I, followed by Western blot using anti-EGFP or anti-V5 antibody to detect associated MAVS and G, respectively. Data are representative of two independent experiments.