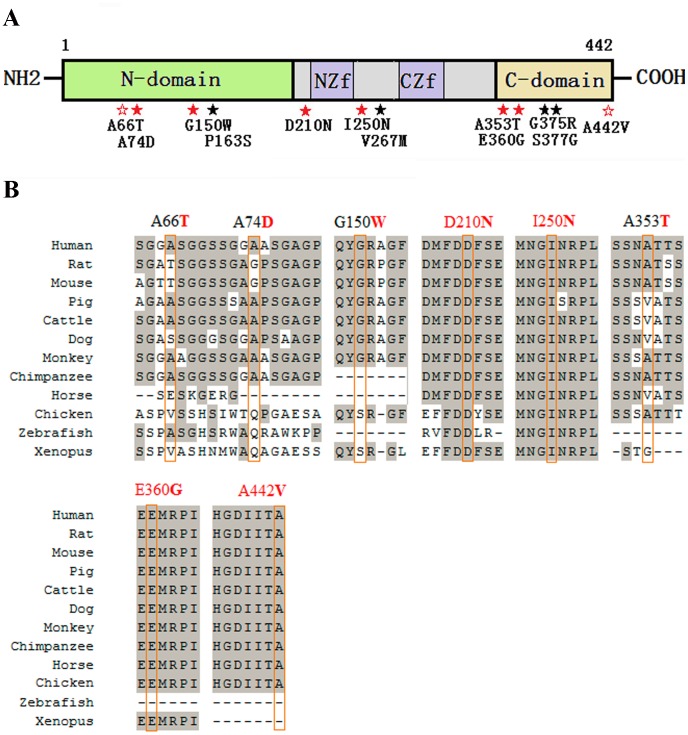
Figure 1. Distribution of the identified GATA4 mutations and multiple sequence alignment across species.
(A) A schematic diagram of the GATA4 protein and the locations of the 12 non-synonymous mutations identified in this study (solid red star indicates a mutation that has not been previously reported; empty red star indicates a CHD-specific mutation that has been previously reported; solid black star indicates a mutation that is also found in controls). N-domain, N terminal domain; NZf, N terminal zinc finger domain; CZf, C terminal zinc finger domain; C-domain, C terminal domain. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the GATA4 protein across different species. The result shows that residues 210 and 250 are highly evolutionarily conserved, and residues 360 and 442 are conserved in mammals.