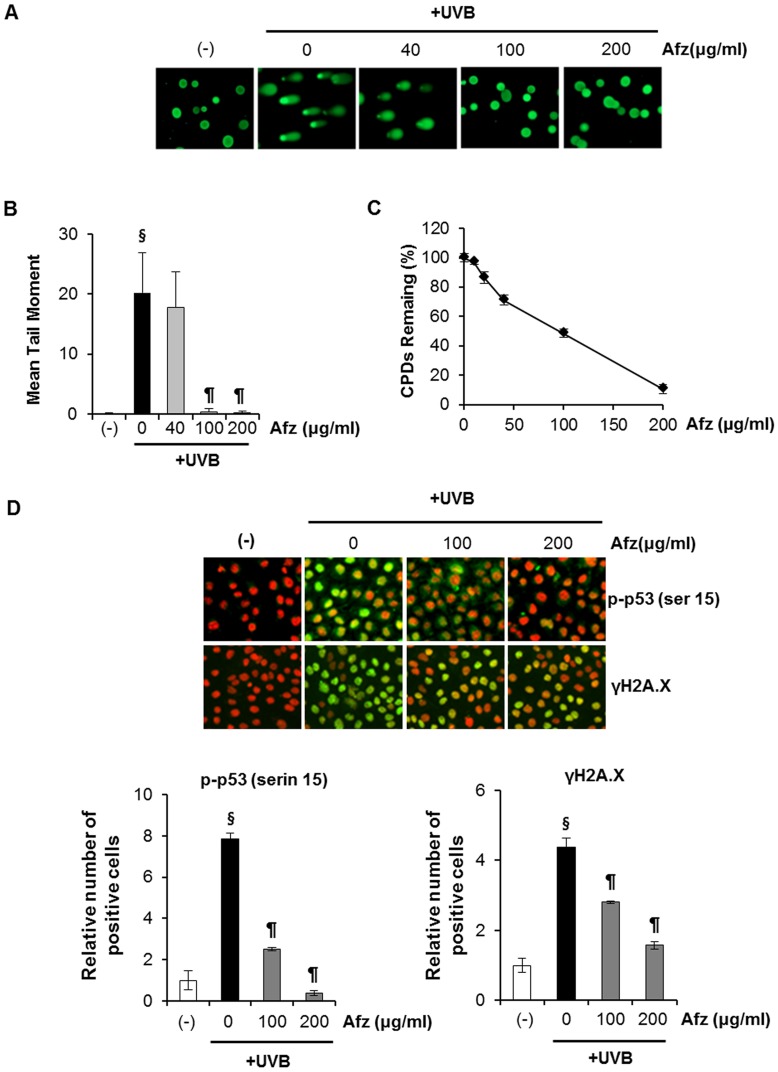
Figure 2. UVB-induced DNA damage is attenuated by the UV-absorbing activity of afzelin itself.
Cells were treated with different concentrations of afzelin (40–200 µg/ml) for 1 h before being exposed to UVB (20 mJ/cm2). A. At 30 min after UVB irradiation, the percentage of cellular DNA damage was detected by the comet assay after rewinding the DNA with alkaline buffer. Slides were stained with SYBR and viewed under a fluorescence microscope. Representative data, n = 3 B. Tail lengths (µm) of a minimum of 50 comets in each sample were analyzed using software image analysis. C. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of the percentage (%) of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) remaining in cells pretreated with vehicle or different concentrations of afzelin (40–200 µg/ml) at 30 min before UVB irradiation (20 mJ/cm2). D. Immunofluorescence analysis of phosphoactive histone H2A.X (γH2A.X; green) and phospho-p53 (serin 15) (green). Staining with propidium iodide (PI; red) was performed to observe cell nuclei. The number of Alexa Fluor 488-positive cells per 100 PI-positive cells was determined in two individual high-power fields per experiment by two independent assessors. Images were analyzed with GE IN Cell Analyzer1000 Workstation software. Data are presented as means ± SD, n = 3 (B-D). § P<0.01 compared with the vehicle-treated group, ¶ P<0.01 compared with the UVB treated group (B–D).