Figure 2. Nanoparticles target lymph node dendritic cells better after i.d. vs. i.m. delivery.
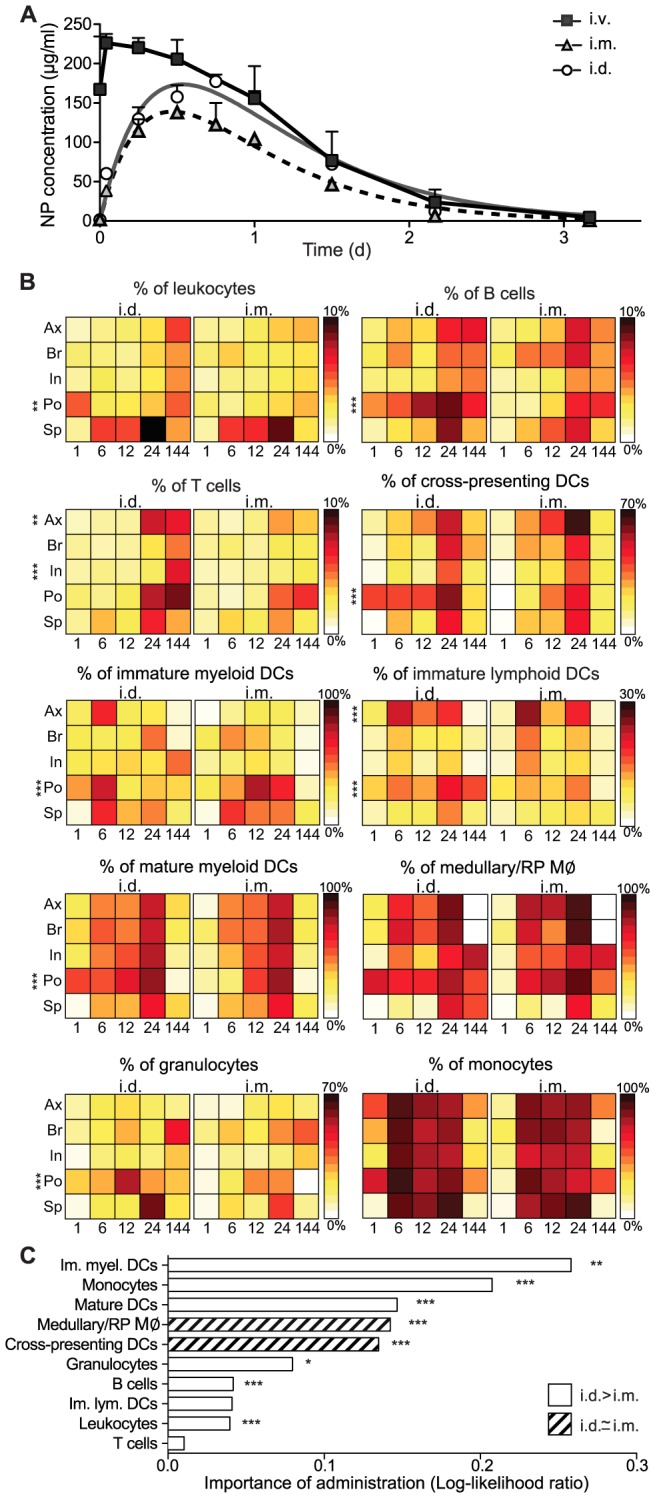
(a) Blood concentrations of Dy649-labeled NPs after i.v., i.m. and i.d. administration. (b) Heat maps representing the median percentage of NP+ cells for indicated cell populations. Note that maxima vary from 10% in total leukocytes to 100% in monocytes. P values were computed by comparing the adjusted means of each organ between i.d. and i.m. for each cell type with a two-tailed Student's t-test. (c) Importance of route of administration for each cellular subtype. The log-likelihood ratio represents the likelihood of the alternate model, i.e. the model without taking account the route of administration, over the likelihood of the full factorial model. P values were computed using the Chi Square test between the alternate model and the full model for each population. For 144 h, n = 2, for all else, n≥4. Leukocytes: CD45+, mature myeloid DCs: CD11c+CD11b+I/Ab+, cross-presenting DCs: CD11c+CD8α+ I/Ab+, immature myeloid DCs: CD11c+CD11b+I/Ab−, immature lymphoid DCs: CD11c+CD11b−I/Ab−, medullary/red pulp (RP) macrophages (MØ): CD11b+F4/80+, monocytes: CD11b+GR1midSSClowF4/80+, granulocytes: CD11b+GR1highSSChigh, T cells: CD3ε+, B cells: B220+. Draining lymph nodes are indicated by Ax: axillary, Br: brachial, In: inguinal, Po: popliteal; Sp: spleen. *p≤0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005.
