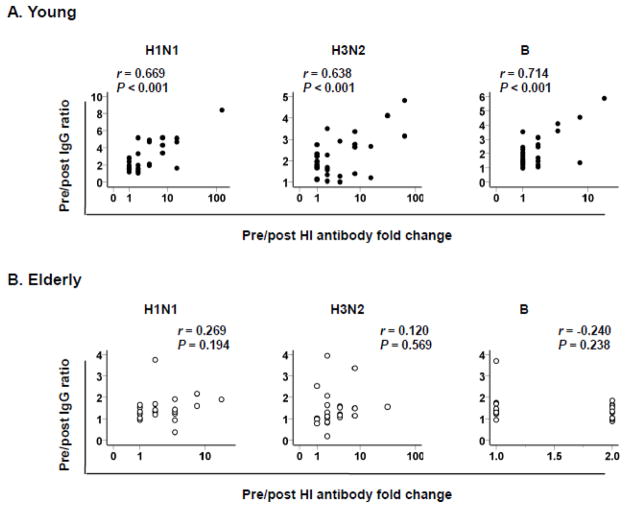
Figure 2. The ratios of pre/post vaccination IgG levels specific for influenza virus strains correlate with the changes in hemagglutinin inhibition (HI) antibody titers in young but not elderly people after influenza vaccination.
(A–B) Serum levels of IgG specific for individual strains of influenza virus included in influenza vaccine 2011–2012 (A/California/7/2009 (H1N1), A/Perth/16/2009 (H3N2) and B/Brisbane/60/2008) were measured in young (n = 29) and elderly (n = 26) adults by ELISA before and ~32 days (range, 29–36 days) after influenza vaccination. Serum HI antibody titers for the same strains of influenza virus were measured by HI assay. (AB) Ratios of Pre/post vaccination IgG levels specific for individual influenza viral strains were correlated with the changes in HI antibody titers in young and elderly people. P values were determined by Pearson correlation analysis.