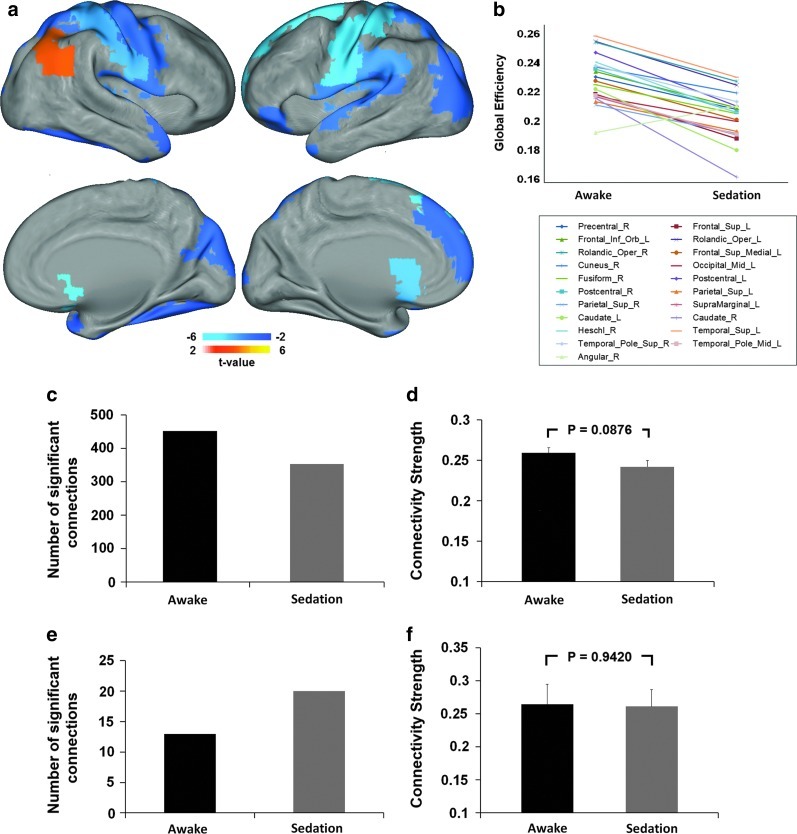
FIG. 4.
Sedation-induced regional global efficiency changes. (a) Regions with significant changes in global efficiency during sedation (p<0.05, FDR corrected); color bars denote t-values from the paired t-tests of the regional global efficiency values (positive: sedation>rest; negative: sedation<rest). (b) Plot of the changes of mean global efficiency from awake resting to sedation for each region showed in (a). (c) Comparison of the number of significant positive connections associated with regions showing decreased global efficiency. (d) Comparison of the strength of the significant positive connections associated with regions showing decreased global efficiency. (e) Comparison of the number of significant positive connections associated with right angular region. (f) Comparison of the strength of the significant positive connections associated with right angular region. Error bars denote standard error of the mean.