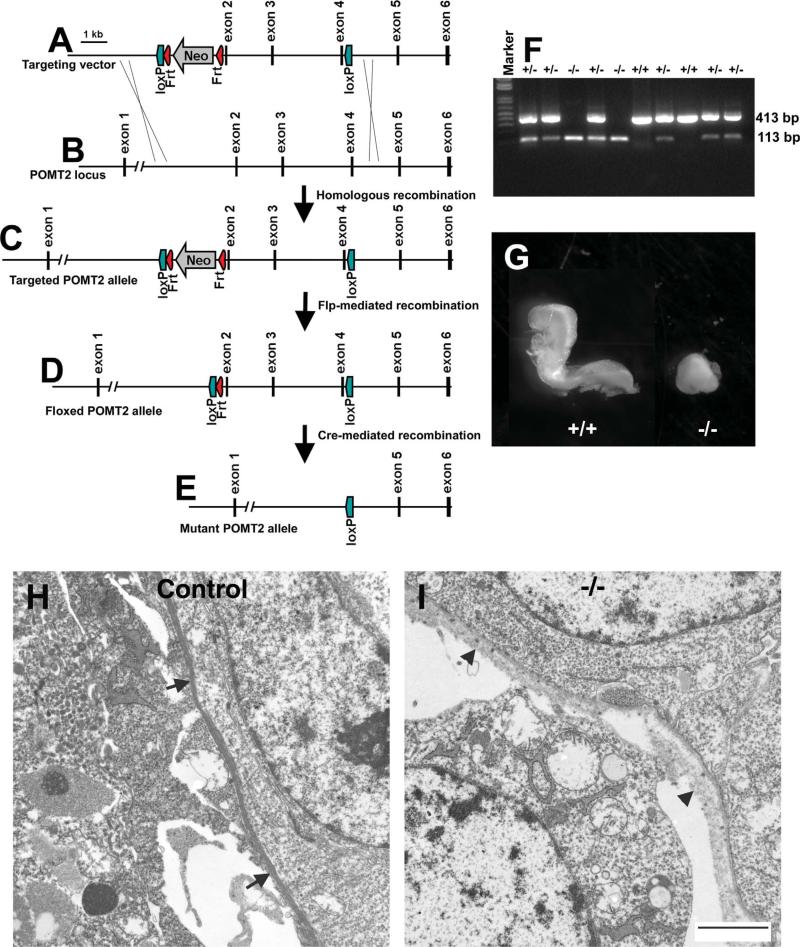
Figure 1.
Targeting construct and the diagram for generation of floxed POMT2 allele. A: Targeting construct: a cassette containing loxP-Frt-Neo-Frt was inserted into intron 1. A second loxP site was inserted into intron 4. Thus, the targeting vector is designed to have exons 2, 3, and 4 flanked by two loxP sequences. Flanking the two loxP sites are homologous sequences of the POMT2 locus. After homologous recombination in ES cells, one of the two POMT2 alleles will become the targeted allele (shown in C). B: Wildtype POMT2 allele. (C) Targeted POMT2 allele. This allele is present in ES cells that underwent homologous recombination with the targeting vector after electroporation of the targeting vector. D: Floxed POMT2 allele. This allele is obtained by crossing chimeric mice with ROSA26-Flp transgenic mice to remove neomycin resistance cassette. E: Mutant POMT2 allele. This allele is obtained after Cre-mediated conditional removal of the floxed sequences (exons 2–4) of the floxed POMT2 allele. F: RT-PCR showed that the knockout embryos expressed only truncated POMT2 mRNA. The RT-PCR product of truncated POMT2 mRNA is 113 bp. G: E8.5 POMT2 null embryos were runted. H,I: Transmission EM analysis of the Reichert's membrane of control and POMT2 null embryos revealed that the POMT2 null Reichert's membrane was less dense with multiple breaks at E6.5 (arrowheads in I). Scale bar = 2 μm in I (applies to H). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]