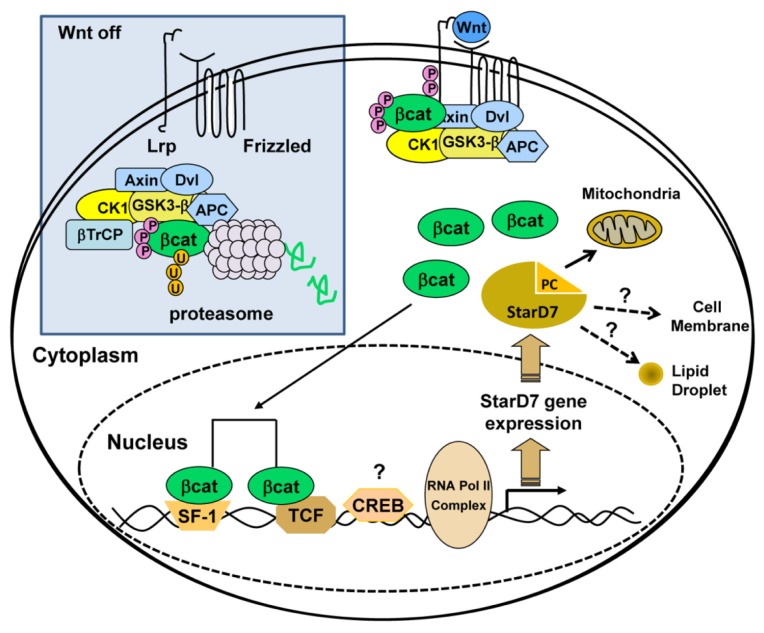
Figure 2.
Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1)/β-catenin upregulates StarD7 expression in JEG-3 cells. The proposed model shows SF-1/β-catenin mechanisms involved in StarD7-induced expression, based on current data. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is a conserved cell-cell signaling mechanism in animals that regulates gene expression via the TCF/LEF1 family to coordinate many cellular processes. In the absence of Wnt signaling, the destruction complex remains in the cytoplasm, where it binds, phosphorylates, and ubiquitinates β-catenin via the β-transducing repeat-containing protein (βTrCP). Finally, the proteasome recycles the complex by degrading β-catenin (Wnt off). In the presence of Wnt signaling, the destruction complex captures and phosphorylates β-catenin but ubiquitination by β-TrCP is blocked. This results in accumulation and nuclear localization of the newly synthesized β-catenin. In the nucleus, β-catenin regulates target gene expression by interacting with TCF/LEF1 transcription factors [69]. Free β-catenin interacts with SF-1 to increase StarD7 transcription [65]. In addition, the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) may bind putative cAMP response elements that modulate gene expression. StarD7 mediates PC intracellular trafficking to the mitochondria [26] and possibly to the plasma membrane [24] and lipid droplets [34]. APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1, casein kinase 1; Dvl, Dishevelled; LrP, low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein.