Figure 1. Loss of cholinergic innervation in GFRα2-KO mouse gastric mucosa.
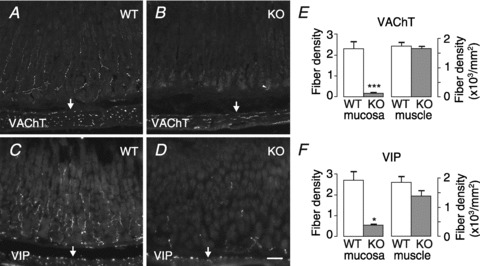
Representative sections from wild-type (WT) and GFRα2-KO (KO) mouse gastric mucosa (oxyntic part) immunostained for VAChT (A and B) and VIP (C and D). A, numerous VAChT-positive cholinergic fibres are seen in wild-type mouse gastric mucosa and in the underlying circular smooth muscle layer. B, density of VAChT-positive nerve fibres is profoundly reduced in the GFRα2-KO mouse gastric mucosa but not in the muscle layer (arrows). Arrowhead marks unspecific staining of gland lumen. C and D, density of VIP-positive nerve fibres is profoundly reduced in the GFRα2-KO mouse gastric mucosa but not in the underlying muscle layer (arrows). The density of VAChT- (E) and VIP- (F) positive fibres in the mucosa (in arbitrary units) and muscle was estimated from wild-type (n= 4–5) and GFRα2-KO (n= 3–4) mice using systematic random sampling. *P= 0.02; ***P= 0.004, using a t test. Scale bar: 50 μm.
