Figure 8.
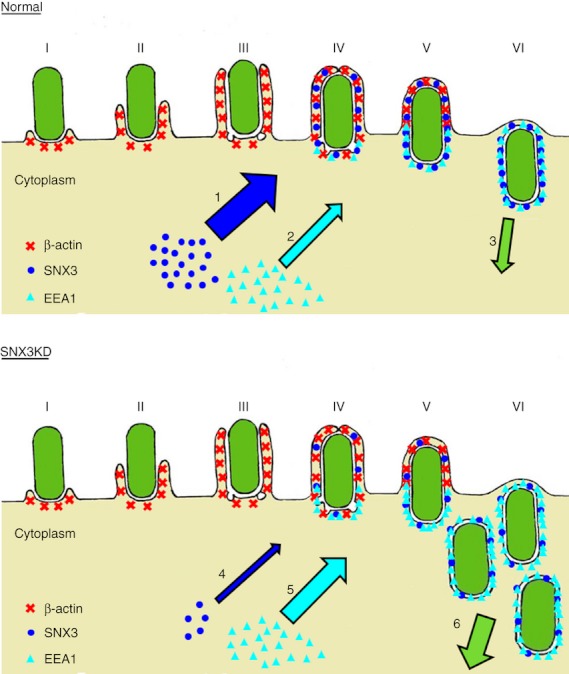
Stages in phagosome formation and a model for the regulation of phagocytosis by sorting nexin 3 (SNX3). Phagocytic cup initiation (I), phagocytic cup extension [(II) and (III)], transitional closure (IV) and nascent phagosome separation from the plasma membrane [(V) and (VI)] are illustrated with emphasis on the recruitment of β-actin (red), SNX3 (blue) and early endosome antigen-1 (EEA1) (cyan). Under normal condition, normal level of SNX3 recruitment to nascent phagosomes (1) keeps the level of EEA1 recruitment to nascent phagosomes in control (2), resulting in a well-regulated input of membrane materials and phagosome formation (3). With the depletion of SNX3 through small-interfering RNA knockdown, a drastic decrease in SNX3 recruitment to nascent phagosomes (4) reduces the competition with EEA1 for binding to the phagosomal membrane, hence an increase in EEA1 recruitment to nascent phagosomes (5). This in turn results in an increase or dysregulated input of membrane materials to the nascent phagosomes, which accelerates the synthesis of phagosomes (6). Thickness of the arrows in the illustration is proportional to the magnitude of the various events described.
