Fig. 3.
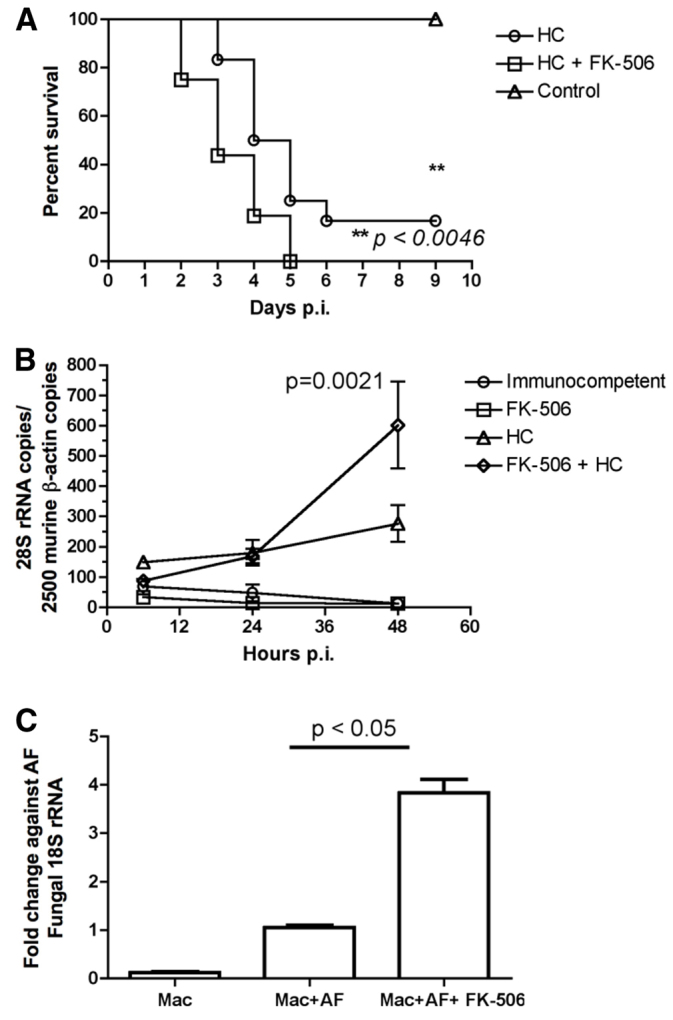
Survival from pulmonary aspergillosis and fungal burden in BALB/c mice immunosuppressed with FK506 and hydrocortisone. (A) Survival from pulmonary aspergillosis. Two groups of eight BALB/c mice were immunosuppressed with either hydrocortisone (125 mg/kg s.c. every 3 days) or with hydrocortisone (125 mg/kg s.c. every 3 days) in combination with FK506 (1 mg/kg i.p. daily) from day −3. They were then intranasally inoculated with 5×106A. fumigatus CEA10 conidia. Data are shown as mean from the two independent experiments. Survival differences were determined by Kaplan-Meier analysis. (B) Time course of pulmonary fungal burden. Groups of three mice were either untreated or immunosuppressed with FK506, hydrocortisone or both and sacrificed at 6, 24 and 48 hours post-infection and lungs harvested. Total DNA was isolated and A. fumigatus fungal burden estimated by semi-quantitative RT-PCR in comparison with murine β-actin. Statistical significance was determined by linear regression analysis. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. (C) Killing of A. fumigatus by murine alveolar macrophages. The alveolar macrophage cell line MH-S was pre-treated either with 10 ng/ml FK506 or with carrier. The ability to kill A. fumigatus CEA10 was assayed at 6 hours post-infection at an MOI of 1 by RT-PCR for fungal RNA after normalisation to control. p.i., post-infection; HC, hydrocortisone; Mac, alveolar macrophage; AF, A. fumigatus.
