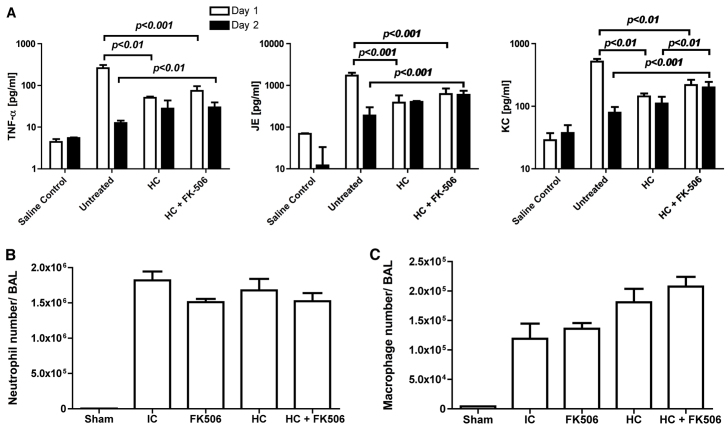
Fig. 6.
Immunosuppression with FK506 and hydrocortisone leads to increased levels of TNFα, JE and KC in the lung in invasive aspergillosis. (A) Groups of three mice were either untreated or immunosuppressed with hydrocortisone or FK506 plus hydrocortisone and culled at 24 and 48 hours after infection with 5×106A. fumigatus CEA10 conidia. Saline controls were uninfected. Lungs were homogenised and supernatant levels of TNFα, JE and KC measured by Luminex MAP analysis. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test. (B,C) Groups of three mice were either untreated or immunosuppressed with FK506, hydrocortisone or both and culled at 24 hours after infection with 5×106A. fumigatus CEA10 conidia. (B) FACS analysis for neutrophil influx into the bronchoalveolar space. There were no significant differences between infected groups. (C) FACS analysis for macrophages in the bronchoalveolar space. There were no significant differences between infected groups. Sham, uninfected group; HC, hydrocortisone; IC, immunocompetent; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage. Data are shown as mean and s.e.m.