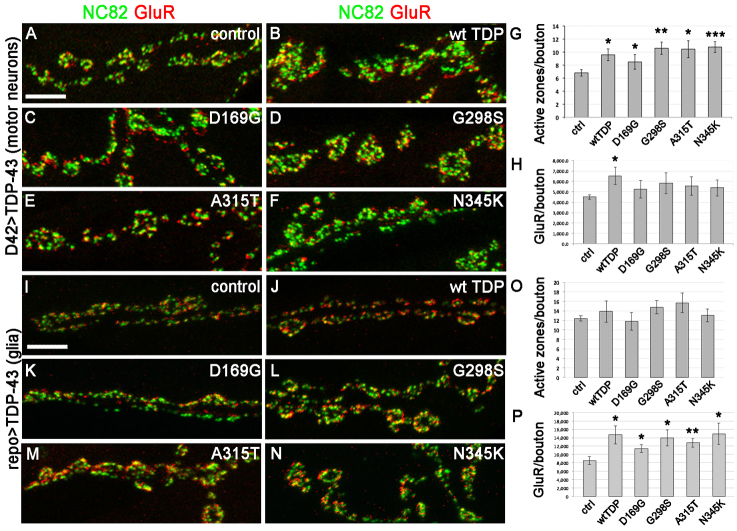
Fig. 6.
Active zones and postsynaptic glutamate receptor distribution are differentially affected at the neuromuscular junction by TDP-43 expression in motor neurons versus glia. (A–F) The presynaptic marker Bruchpilot (visualized with NC82 antibodies) and postsynaptic marker glutamate receptor (GluR) were used to label neuromuscular junctions in larvae expressing TDP-43 in motor neurons (staining and genotype as indicated). (G,H) Quantification of NC82 puncta indicates a significant increase in the number of presynaptic active zones per bouton (G), which is not accompanied by a similar increase in postsynaptic GluR (except for wild-type TDP, see H). (I–N) The presynaptic marker Bruchpilot (visualized with NC82 antibodies) and postsynaptic marker GluR label neuromuscular junctions in larvae expressing TDP-43 in glia (staining and genotype as indicated). (O,P) Quantification of NC82 puncta shows no effect on the number of presynaptic active zones per bouton (O), but a significant increase in postsynaptic GluR expression (P). Values show means ± s.e.m. All comparisons were performed using Gal4 driver controls and Student’s t-test was used to calculate significance; *P<0.5, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Scale bars: 5 μm.