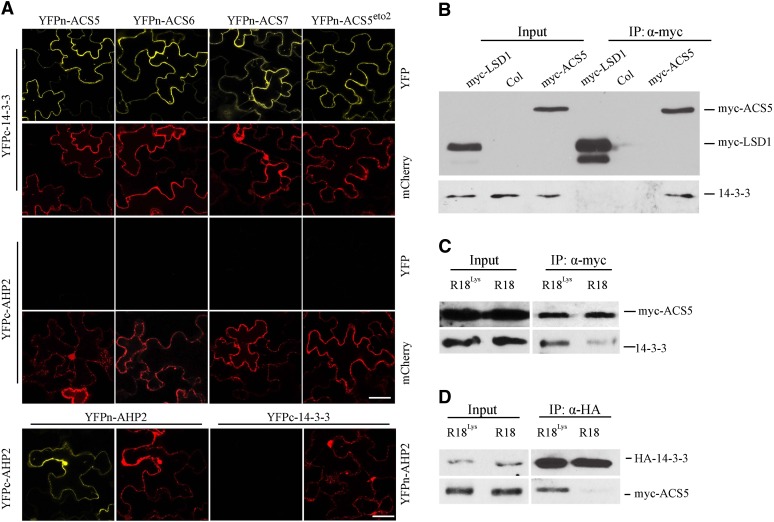
Figure 1.
14-3-3 Interacts with All Three Classes of ACC Synthases.
(A) BiFC of 14-3-3ω and various ACS isoforms in transiently transformed N. benthamiana. A plasmid expressing a mitochondria, monomeric cherry (mCherry) fluorescent protein was used as a transformation marker. YFPc-AHP2 and YFPn-AHP2 were used as negative control, which were shown to be expressed by their ability to dimerize and produce a BiFC signal. The YFP signal was observed using confocal microscopy. Bars = 50 µm.
(B) Coimmunoprecipitation of 14-3-3 and ACS5. Protein extracts from light-grown seedlings expressing myc-ACS5 and myc-LSD 1 were immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc antibody and the immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by protein gel blotting using an anti-myc or anti-14-3-3 antibody. The myc-LSD1 was used as a negative control.
(C) R18 peptide disrupts the interaction of ACS5 and 14-3-3 proteins in seedlings. Protein extracts from Arabidopsis seedlings expressing myc-ACS5 treated with 20 µg/mL R18 or R18Lys for 3 h were immunoprecipitated with an anti-myc antibody, and the immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by protein gel blotting using an anti-myc or anti-14-3-3 antibody.
(D) R18 peptide disrupts the interaction of ACS5 and 14-3-3 proteins in protoplasts. Protein extracts from protoplasts expressing HA-14-3-3ω and myc-ACS5 proteins that were treated for 3 h with 10 µg/mL R18 or R18Lys were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody, and the immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by protein gel blotting using an anti-myc or anti-HA antibody.