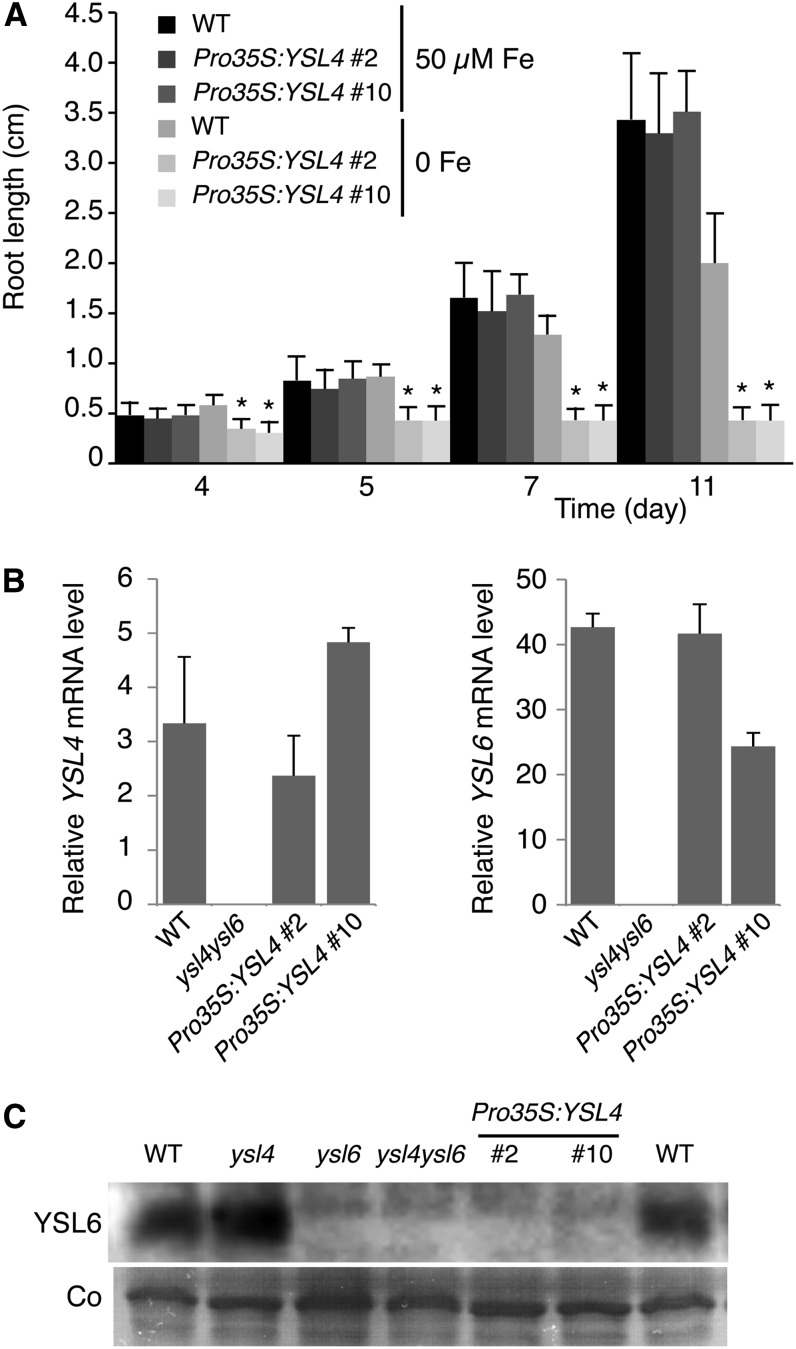
Figure 8.
Ubiquitous Expression of YSL4 Dramatically Decreases Plant Tolerance to Iron Deficiency and Inhibits YSL6 Synthesis.
(A) Time-course study of primary root elongation of two independent Pro35S:YSL4 lines (#2 and #10) in the ysl4 mutant background, grown in iron-replete (50 µM) or iron-deficient (no added iron) medium showing increased inhibition of primary root elongation by iron deficiency in the transgenic lines. Error bars represent sd. Asterisk indicates significant difference between wild-type (WT) and ysl4/Pro35S:YSL4 plants, P < 0.001; measurements were obtained from 25 plants from each of three separate experiments (Student’s t test).
(B) Expression of YSL4 and YSL6 genes in Pro35S:YSL4 lines. Real-time RT-PCR was performed on 7-d-old iron-replete plants from experiment (A). Measurements were made in triplicate from two independent experiments. Error bars represent sd.
(C) Ubiquitous expression of YSL4 inhibits YSL6 protein accumulation. Immunoblot analysis was performed on 7-d-old iron-replete plants from experiment (A). Total microsomal proteins were hybridized with anti-YLS6 antibody. Coomassie blue staining (Co) was used as loading control.